(August 1954 – November 1954: Young Romance #72 – #74, Young Love #60 – #62, Young Brides #18 & #19, In Love #1 & #2)
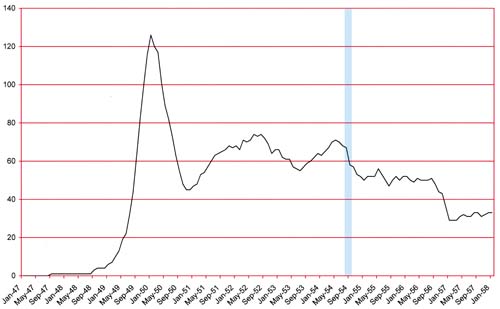
Number of Romance Titles 1947 – 1958 (the period covered in this chapter is shaded in blue)
As can be seen in the above chart romance comics had entered into a decline during this period. Did Joe Simon and Jack Kirby notice this? Had they been observant they might have for as will be shown they benefited from the failure of other titles. But then again there were always fluctuations in the number of titles and publishers so perhaps Joe and Jack were not aware that things had become very different. Or perhaps they were too caught up in their own business to notice the bigger picture. August 1954 (cover date) marked the release of Bullseye the first title for Mainline, Simon and Kirby’s own publishing company. In Love, the romance title for Mainline, would be released in September. Starting their own publishing company was a big step for Simon and Kirby but unfortunately their timing was particularly bad.
In chapter 27 I noted the appearance of some new artists in the Simon and Kirby productions (unfortunately as of yet unidentified). The art covered in the last chapter was created by 8 artists which in itself was an increase over the earlier period. I have identified 12 artists for the period covered by this chapter and that does not include unidentified artists. There are more pages of unattributed art than those by any identified artist. Frankly I have not sorted them all out but I believe that there are at least 5 or 6 artists that I cannot identify. A couple of these additions to the studio had appeared previously in Simon and Kirby productions and almost all would only provide a few pieces before disappearing from the studio. Oddly one artist, Bob McCarty, who played an important part in the two previous chapters, is completely missing in this one. However McCarty will be returning in future chapters.
The artist line-up based on their productivity was Bill Draut (42 pages), John Prentice (41 pages), Jack Kirby (25 pages), Mort Meskin (20 pages), Art Gates (19 pages) with Leonard Starr and Jo Albistur tied (12 pages). The rest of the artists provide a single story or a small number of single page features. There are 65 pages by unidentified artists but as I wrote above these were distributed among 5 or more artists.
With one exception the covers for the Prize romance titles were done by Draut and Prentice. As seen previously, some of the covers were made from stats of a splash panel (or visa versa). The one exception is the cover of Young Brides #19 (November 1954) which I have tentatively attributed to Joe Simon. This assignment is not based on art style but rather on evidence from Joe Simon’s art collection. I hope that someday I will be able to write about this cover.

In Love #1 (September 1954) “Bride of the Star” Chapter 1 “The First Pang of Love”, art by Jack Kirby
As I promised last chapter, Jack Kirby returns to romance comics after a short absence. However he appears only in Mainline’s In Love and not in any of the Prize romance titles. Kirby’s absence from Prize romances will continue for some time. In Love was an interesting title whose “hook” was the long story contained in each issue. Kirby did all 20 pages of the art for the “Bride of the Star” from In Love #1. I will not write much about this story here because I covered it in a previous post on In Love #1.
Besides the length of the story, one of the things that distinguish In Love from the Prize romance titles is that Jack returns to full page splashes for all the three chapters. Frankly I already illustrated the best splash in my previous post but I felt I must include one of the other ones here. To be honest it is not one of Kirby’s best pieces but I feel that the splash for the other chapter to be even more inferior. But all of the story art is actually quite good.
Kirby on contributed a small part to the featured story “Marilyn’s Men” from In Love #2 (November 1954) with most of the work being done by Bill Draut. Since the post whose link I provided covers this story I will forego further comments here.
The cover for In Love #1 was one of the rare collaborations between Jack Kirby and an artist other the Joe Simon, in this case John Prentice (Jerry Robinson at the Jack Kirby Tribute Panel). Not only was the cover drawn by different artists but inked by different hands as well. Prentice’s back was clearly inked by himself and I suspect, though I am by no means certain, that Jack inked his own pencils as well.
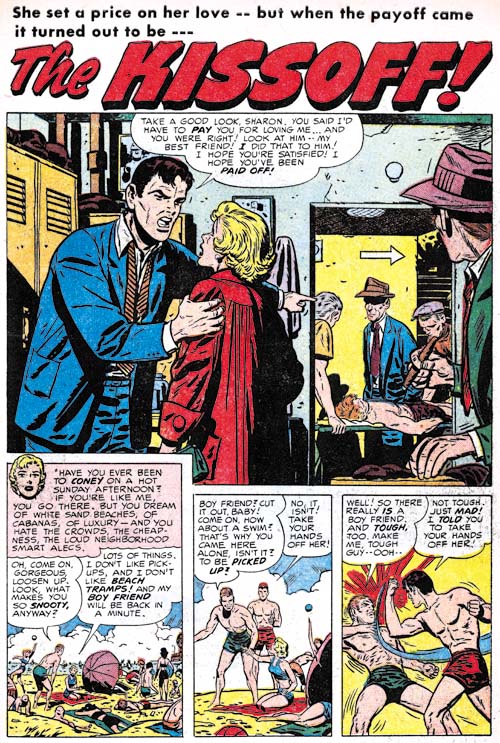
Young Romance #74 (November 1954) “The Kissoff”, art by Bill Draut
Bill Draut was the most prolific artist during this period but not by much. His recent decreased presence in S&K productions is a bit hard to understand. I once surmised that it might be due because of the work he was doing in preparation for the launch of Mainline. But on reflection there just does not seem enough work by Draut in those early issues of the Mainline comics to impact his normal work load. So I now suppose that his recent decreased contribution was due to some personal reason. Draut is one of the more consistent artists to work for Simon and Kirby but his style did not change much over the years. This makes it difficult to have new things to say about him. The same link I provided above for my post on In Love #2 goes into more detail about Draut’s work on “Marilyn’s Men”. I also did a post (Swiping Off of Kirby) about the use Bill made of art from an earlier story by Kirby.

Young Romance #73 (September 1954) “Girl from the Old Country”, art by John Prentice
John Prentice was just behind Draut in productivity. This is one of the examples where a stat of the splash for this story was used to create the cover. Note that while story splashes were no longer being used in the Prize romance titles, Prentice is still providing a smaller than typical splash panel.

Young Love #60 (August 1954) “Outcast”, art by Mort Meskin
There was an unexpected surge in productivity by Meskin in the last chapter and now there is a just as sudden drop in his output. I must admit that I am a little perplexed about what is going on with Mort. He was working for other publishers and that suggests that he was no longer working in the actual Simon and Kirby studio. But how does one explain the ups and downs since then? I have heard of discussion somewhere on the web where it has been suggested that when Meskin left the S&K studio to work in his own studio that Mort was once again plagued with difficulties in starting work on a blank page. I have no way of saying whether this is true but perhaps it would explain his varied, but often unusually low, output in Simon and Kirby productions. Even if Meskin’s productivity was poor during this period he still did some very nice work. “Outcast” is a good example of a real nice piece by Meskin (I believe he inked it as well). I previously posted on a Mort’s “After the Honey-Moon” from In Love #1 which while very short is one of his masterpieces.

Young Brides #18 (September 1954) “My Cheating Heart”, art by Mort Meskin
“My Cheating Heart” is another great piece by Mort Meskin. I particularly like the inking in this piece. The solid blacks are used very effectively. I am pretty sure this is not Meskin’s own inking or that of George Roussos either but I cannot suggest who the inker was.

Young Romance #74 (November 1954) “A Holiday for Love”, art by Art Gates
Art Gates continue to supply numerous single page features but he is also did a few 3 page stories. At 6 pages, “A Holiday for Love” is the longest work Gates has yet done for Simon and Kirby. I cannot say that Art is one of my favorite Simon and Kirby artists but I admire the way he can do pieces like this a more cartoon-like gag features as well.

Young Love #61 (September 1954) “Miss Moneybags”, art by Leonard Starr
Leonard Starr was not a new artist for Simon and Kirby productions but a returning one. He played an important part in the Prize romance titles for a little under two years ending in February 1951. His style has not changed that much during his absence and even without a signature “Miss Moneybags” (Young Love #61, September 1954) and “Cinderella’s Sisters” (Young Love #62, November 1954) were clearly done by Starr. However Leonard style had evolved somewhat so it is just as clear that this is not left over material. Although Starr was no longer using page formats that provided a series of tall and narrow panels he still had a predilection for such panels and was using alternative ways to introduce them. While it is possible that the reviews I perform for future chapters of this serial post may uncover one or two other stories by Starr, I am pretty confident that there will not be more than that. Leonard Starr would be like a number of artists from this chapter in that he made a brief appearance and then disappeared from Simon and Kirby productions. In Starr’s case he would be starting his own syndication strip, “Mary Perkins on Stage”, in a year or so.

Young Love #61 (September 1954) “Mother Never Told Me”, art by George Roussos?
I am by no means certain, but “Mother Never Told Me” looks like it might have been done by George Roussos. The resemblance is mostly in the men with the woman reminding a little bit like the work of Marvin Stein. But overall I believe the Roussos seems the best fit. George last appeared in a Simon and Kirby production in Black Magic #24 (May 1953). If this attribution is correct, Roussos like Starr will not appear in a future Simon and Kirby productions.

Young Romance #73 (September 1954) “Afraid of Marriage”, art by Jo Albistur
Although unsigned, “Afraid of Marriage” and “Just For Kicks” (Young Love #61, September 1954) are both clearly the work of Joaquin Albistur (he also appeared in Police Trap #1 in this same month). I had previously used Joe as the first name for this artist but it is now clear that he was an artist from Argentine (Joaquin Albistur the Same As Joe Albistur?). Joe Simon does not remember Albistur by name, but he does recollect someone from South America doing work for Simon and Kirby. Most people assume Simon was thinking of Bruno Premiani, but I believe it is even more likely that it was Albistur that Joe was recalling.
Unlike most of the new artists in this chapter, Albistur will play an important part in Simon and Kirby productions in the coming year. Jo is not well known among fans and I am not sure how much comic book work he did outside of Simon and Kirby productions. I have seen some original art from “The World Around Us” from 1961 that has been attributed to Albistur. I am not convinced but if it was his work Albistur had adopted a particularly unpleasing dry style. Despite Jo’s short time working for Simon and Kirby he is one of my favorite studio artists. His woman have an earthy beauty that I like, he had an eye for gestures, used interesting compositions and was skillful at graphically telling a story.

Young Love #62 (November 1954) “Too Darned Innocent”, art by W. G. Hargis
There is one signed piece by W. G. Hargis, “Too Darned Innocent”. However given the number of unidentified artists appearing in Simon and Kirby productions there is the distinct possibility that other unsigned worked may have been done by Hargis during this period as well. In fact I have heard of suggestions that Hargis may have been responsible for a story in Police Trap.

In Love #2 (November 1954) “Mother by Proxy”, art by Tom Scheuer
Tom Scheuer is another artist that only did one signed work for Simon and Kirby. Scheuer (who much later changed his name to Sawyer) is perhaps better known for his advertisement comic work (see For Boys Only from Those Fabulous Fifties and Comic Strip Ad Artist Tom Scheuer from Today’s Inspirations; both great blogs).
Joe Simon’s collection includes the original art for a page from this story. On the back is the name Art Sehrby, a telephone number and a street address. This raises the possibility that Simon and Kirby obtained Scheuer’s piece, and perhaps those of some other artists, from an agent.

Young Brides #19 (November 1954) “Love for Sale”, pencils by Ross Andru, inks by Martin Thall
There is a story behind “Love for Sale” that has been discussed on the Kirby list but I do not believe I have written about in my blog. Mike Esposito and Ross Andru launched their own publishing company Mikeross with their earliest comic having a cover date of December 1953 (3-D Love). This then was well in advance of Simon and Kirby’s Mainline Comics whose first issue (Bullseye) came out in August.
Mikeross only published four titles (3-D Love, 3-D Romance, Get Lost and Heart and Soul. The 3-D romance titles were single issues and I suspect that their timing was a little off. The initial 3D comics sold very well but were apparently a novelty item. My understanding is that Simon and Kirby’s Captain 3-D which came out in December 1953 was already a bit late and sales were not that great. Since the Mikeross 3D romance titles have cover dates of December and January, I suspect they suffered from lower sales as well. Get Lost went to issue #3 while Heart and Soul only lasted to issue #2. Usually when a title is cancelled after just 2 or 3 issues it is a sign that something other than poor sales was involved. I suspect that the returns from their first comic, 3-D Love were so poor that the distributor pulled the plug on the whole deal.
I do not have the biography of Mike Esposito that came out a few years ago but I did have the chance to flip through it to see what he had to say about what happened next. If I remember correctly Esposito claimed that the distributor forced them to hand over their unpublished artwork to Simon and Kirby. Frankly this is a pretty suspicious claim because a distributor does not have any legal claim to the artwork. Further in my discussions with Joe Simon he has vigorously denied that it happened. Martin Thall gave an interview published in Alter Ego #52 where he stated that in order to recover some money they sold some art to Simon and Kirby and that Kirby was the one who arranged and received it. This makes a lot more sense and is the version that I accept.
The last issue of Heart and Soul was cover dated June so the next one would be expected for August. “Love for Sale” was used in Young Brides #19 (November). The timing is so perfect that there is little doubt that this story was among the art sold to Simon and Kirby. What makes that even more convincing is that the lettering was not done by Ben Oda like almost all of Simon and Kirby’s productions.
This is not Ross Andru’s first appearance in Simon and Kirby productions as a story by him appeared in May 1952 (Chapter 16) and two in May and June of 1953 (Chapter 19). Another Andru story will be seen in the next chapter which also was probably bought from the defunct Mikeross publishing company.

Young Brides #19 (November 1954) “Telephone Romeo”, art by unidentified artist
Since one story from Mikeross has been identified the question becomes can any others be found? Such art need not have been used right away but it is interesting that Young Brides #19 contains another story, “Telephone Romeo” that was not lettered by Ben Oda. However the letterer is not the same one that did “Love for Sale”. I have only examined the 3-D Love, 3-D Romance and Heart and Soul #1 but none of them used this artist. Actually I find Andru’s hand through most of them and I suspect Ross and Mike did all the art themselves. So it cannot be said with any certainty that “Telephone Romeo” was another piece sold by Mikeross but it can be confidently said that is was bought from some distressed publisher or artist stuck with unused art.
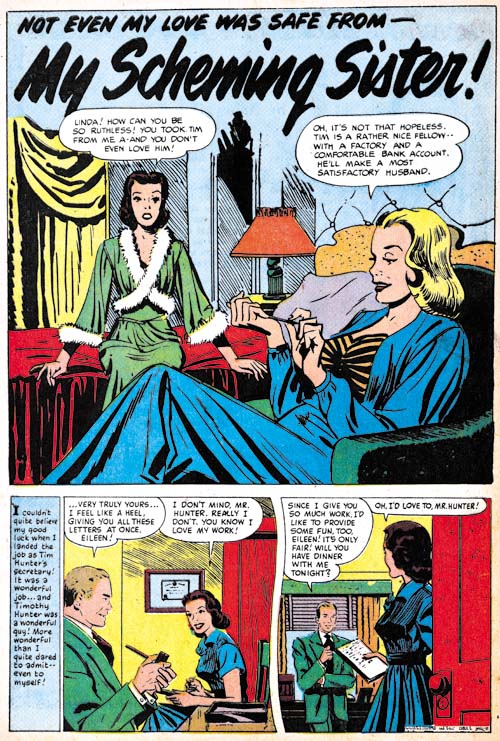
Young Love #62 (November 1954) “My Scheming Sister”, art by unidentified artist
There is yet another piece, “My Scheming Sister”, with lettering clearly not done by Ben Oda. Look at the caption to the first story panel, Simon and Kirby productions did not typically use lower case letters in their captions. Once again this was a piece bought by Simon and Kirby but not necessarily from Mikeross. Whoever the artist was he was one of the better of the unknowns from this period. A smooth confident line and great characterization.

Young Romance #72 (August 1954) “Reform School Babe”, art by unidentified artist
Not all the unidentified artists were new; the one that did “Reform School Babe” had been an important contributor to Simon and Kirby productions for some months. I believe one of my commenters suggested Vince Colletta, at least for the inking, but I am not sufficiently knowledgeable about that artist/inker to hazard a guess.

Young Romance #74 (November 1954) “Idol Worship”, art by unidentified artist
I will not be supplying examples of all the unidentified artists from these romance titles as I have not sorted them all out and anyway some are not that great. But I did want to provide an image from “Idol Worship” by one of the better artists working at this time for Simon and Kirby.
In summary, Simon and Kirby were using a number of new artists. Some like Jo Albistur would play important contribution to S&K productions; others like Tom Scheuer would make a brief appearance and not be seen again. Some may have been hired from the street but there is also the suggestion that some work may have come from an art agent. Further there is good evidence that some of the work came from the failed Mikeross publishing and perhaps other publishers as well. I have not yet done a review of Ben Oda’s lettering like I have those by Joe Simon, Jack Kirby and Howard Ferguson. I suspect a careful comparison of Ben Oda’s lettering with that used in the stories from this period will reveal others that came from romance titles that were failed. Simon and Kirby’s use of such material is not surprising because they had previously obtained art from Harvey after the love glut (Chapter 13, Romance Bottoms Out).
Chapter 1, A New Genre (YR #1 – #4)
Chapter 2, Early Artists (YR #1 – #4)
Chapter 3, The Field No Longer Their’s Alone (YR #5 – #8)
Chapter 4, An Explosion of Romance (YR #9 – #12, YL #1 – #4)
Chapter 5, New Talent (YR #9 – 12, YL #1 – #4)
Chapter 6, Love on the Range (RWR #1 – #7, WL #1 – #6)
Chapter 7, More Love on the Range (RWR #1 – #7, WL #1 – #6)
Chapter 8, Kirby on the Range? (RWR #1 – #7, WL #1 – #6)
Chapter 9, More Romance (YR #13 – #16, YL #5 – #6)
Chapter 10, The Peak of the Love Glut (YR #17 – #20, YL #7 – #8)
Chapter 11, After the Glut (YR #21 – #23, YL #9 – #10)
Chapter 12, A Smaller Studio (YR #24 – #26, YL #12 – #14)
Chapter 13, Romance Bottoms Out (YR #27 – #29, YL #15 – #17)
Chapter 14, The Third Suspect (YR #30 – #32, YL #18 – #20)
Chapter 15, The Action of Romance (YR #33 – #35, YL #21 – #23)
Chapter 16, Someone Old and Someone New (YR #36 – #38, YL #24 – #26)
Chapter 17, The Assistant (YR #39 – #41, YL #27 – #29)
Chapter 18, Meskin Takes Over (YR #42 – #44, YL #30 – #32)
Chapter 19, More Artists (YR #45 – #47, YL #33 – #35)
Chapter 20, Romance Still Matters (YR #48 – #50, YL #36 – #38, YB #1)
Chapter 21, Roussos Messes Up (YR #51 – #53, YL #39 – #41, YB #2 – 3)
Chapter 22, He’s the Man (YR #54 – #56, YL #42 – #44, YB #4)
Chapter 23, New Ways of Doing Things (YR #57 – #59, YL #45 – #47, YB #5 – #6)
Chapter 24, A New Artist (YR #60 – #62, YL #48 – #50, YB #7 – #8)
Chapter 25, More New Faces (YR #63 – #65, YLe #51 – #53, YB #9 – #11)
Chapter 26, Goodbye Jack (YR #66 – #68, YL #54 – #56, YB #12 – #14)
Chapter 27, The Return of Mort (YR #69 – #71, YL #57 – #59, YB #15 – #17)
Chapter 28, A Glut of Artists (YR #72 – #74, YL #60 – #62, YB #18 & #19, IL #1 & #2)
Chapter 29, Trouble Begins (YR #75 – #77, YL #63 – #65, YB #20 – #22, IL #3 – #5)
Chapter 30, Transition (YR #78 – #80, YL #66 – #68, YBs #23 – #25, IL #6, ILY #7)
Chapter 30, Appendix (YB #23)
Chapter 31, Kirby, Kirby and More Kirby (YR #81 – #82, YL #69 – #70, YB #26 – #27)
Chapter 32, The Kirby Beat Goes On (YR #83 – #84, YL #71 – #72, YB #28 – #29)
Chapter 33, End of an Era (YR #85 – #87, YL #73, YB #30, AFL #1)
Chapter 34, A New Prize Title (YR #88 – #91, AFL #2 – #5, PL #1 – #2)
Chapter 35, Settling In ( YR #92 – #94, AFL #6 – #8, PL #3 – #5)
Appendix, J.O. Is Joe Orlando
Chapter 36, More Kirby (YR #95 – #97, AFL #9 – #11, PL #6 – #8)
Chapter 37, Some Surprises (YR #98 – #100, AFL #12 – #14, PL #9 – #11)
Chapter 38, All Things Must End (YR #101 – #103, AFL #15 – #17, PL #12 – #14)