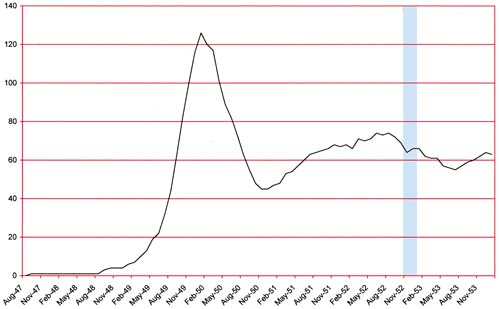
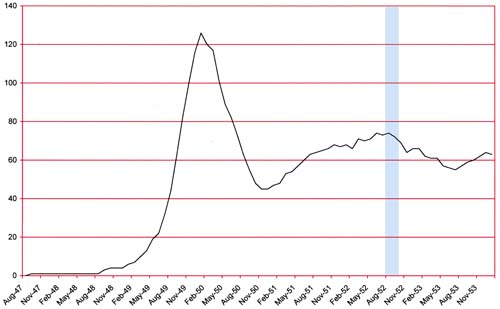
(February 1953 – April 1953, Black Magic #21 – #23)
Just like in the romance titles from this same period, Kirby toke a commanding lead in the amount of art provided for Black Magic (24 pages). Second place fell to Al Eadeh(?) (17 pages), followed by Bill Draut (12 pages) Bob McCarty(?) (10 pages). Mort Meskin, John Prentice, George Roussos and Bill Walton all provided a single story each. There are three short works for which I have not been able to determine the artist. The romance art from this period was almost entirely done by Kirby, Draut, Meskin and Prentice with a single piece by Eadeh. It is interesting therefore that during this period McCarty, Walton and Roussos only provided work in the horror genre title.

Black Magic #21 (February 1953) “The Feathered Serpent”, art by Jack Kirby
Jack Kirby was not only the most prolific Black Magic artist during this period he also did all of the most important work; all the covers and featured stories. No full page splashes but still some rather nice art. I like most of the artists who worked on Black Magic but in all honesty no one other than on Kirby was capable of making a truly interesting monster. This is not as much of a defect for the title as it might seem because few stories had monsters or demon antagonists. Black Magic was more oriented toward the supernatural and not true horror.

Black Magic #23 (April 1953) “Those Who Are About To Die” page 2, art by Jack Kirby
Part of Kirby’s reputation is that he really was not very good at drawing beautiful women. I have to admit I find little variation in the females that he depicted later in his career. I am not sure if Kirby was always to blame for this or if much of it was the result of “corrections” performed by some of his inkers. However during the period he worked with Joe Simon, Jack penciled quite a variety of women. The wife of the painter in “Those Who Are about to Die” is one of my favorites. Both devoted and intellectual she fits perfectly into the part she plays in the story. As far as I am concerned she is just one of the many different beautiful women Kirby drew.

Black Magic #22 (March 1953) “Barbados Burial Vault”, art by Bill Draut
Bill Draut did more than his fair share of good splashes but perhaps his best from this period is the one from “Barbados Burial Vault”. It really does not demonstrate his talent as a penciller; the figures are all rather small and the simple architecture dominates the scene. It is Bill’s willingness to abandon his typical draftsmanship to achieve a mod is what makes this work so appealing to me. The impact is provided by the contrast of the small procession carrying the casket from the bright light of day into the dim burial vault.

Black Magic #22 (March 1953) “Horrible Herman”, art by John Prentice
Perhaps the best story from this period was Prentice’s “Horrible Herman”. John spent most of his time when work for Simon and Kirby with doing romance stories but I feel he had a real talent for horror. Not that this was true horror but rather more of a suspense concerning a boy with great powers. No one could stop Herman, or could they?

Black Magic #23 (April 1953) “Land of the Dead”, art by Mort Meskin
Mort Meskin drew some great splashes in Black Magic but perhaps none of them were more unusual than the one for “Land of the Dead”. It is not that his drawing itself was so technically superior, if anything it was a little bit below his usual work. However Mort has managed to invest this splash with a sense of other-worldliness. No speech balloons but none are required to explain the confrontation of a woman and two eerie figures that block her from a tombstone bearing the words “Here Lies Loves”. The bizarre cloud formations complete the effect imparted to the splash.
This story would have been more appropriate for the by now defunct Strange World of Your Dreams title. Not only would it have been appropriate, this story was almost certainly originally meant for the unpublished fifth issue of that title that would have been published just a few months before. A repeating feature in SWYD was “Send Us Your Dreams” with a pipe smoking Richard Temple doing the dream analysis. The same character is found in “Land of the Dead” except his name has been changed to Bart Roberts. That this was in fact just a substitution can be seen in how that name was just pasted over the older version in the caption of the first story panel (note how the name in is not aligned with the rest of the caption).

Black Magic #21 (February 1953) “Warning Voice”, art by Bob McCarty(?)
Many of the Black Magic stories from this period are rather short. “Warning Voice” is only three pages. Perhaps that is why such a small splash panel was used. The panel is hardly wider than the first story panel and at a glance could be mistaken as the first story panel. While I can see the logic behind such a small splash panel I do not feel it was a good approach due to the confusion it causes.
Note the large eyes particularly in the close-up panel. This remains the chief reason that I am not yet comfortable with the Bob McCarty attribution that I have been following.

Black Magic #21 (February 1953) “The Mind Reader”, art by George Roussos
There is only a single two page story by George Roussos. Observe the Meskin influence that can be seen in the man in the last two panels. I do believe this is an influence and not an indication of actual involvement by Meskin.

Black Magic #22 (March 1953) “Stanwick’s Theory”, art by Bill Walton
I admit than generally I am not overly fond of Bill Walton’s art. He was a competent artist but he only occasionally produces something that really grabs my attention. The splash for “Stanwick’s Theory” is a pleasant exception. In fact I really, really like this splash. The use of a tall narrow panel and extreme close-up and cropping are very effective. Even the cigarette and its smoke play an important part in the composition. This splash is not only unique for Walton it is also rather unusual for Simon and Kirby productions.

Black Magic #23 (April 1953) “Evil Spirit”, art by Al Eadeh(?)
Al Eadeh(?) really made good use of the script for “Evil Spirit”. The image of a beautiful woman using her long hair to strangle a man is certainly memorable. So memorable that years later Jack Kirby would re-use the concept for Medusa a villain (who later becomes a heroine) in the Fantastic Four comic book.