(November 1950 – January 1951: Young Romance #27 – #29, Young Love #15 – #17)
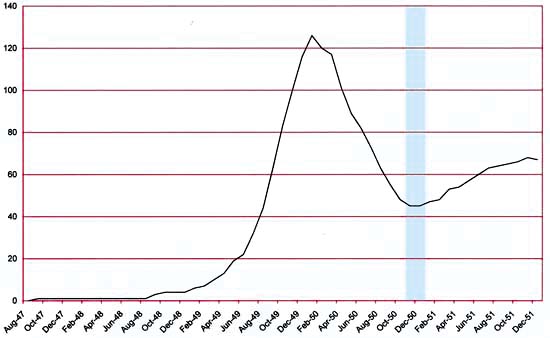
Number of Romance Titles 1947 – 1951 (the period covered in this chapter shaded in blue)
Besides the monthly Young Romance and Young Love, Simon and Kirby were now also producing bimonthly titles Black Magic for Prize and Boys’ Ranch for Harvey. Boys’ Ranch was the first work that Joe and Jack had done for Harvey since Stuntman and Boy Explorers were cancelled in 1946 (other Simon and Kirby features that Harvey had published since then were inventoried material left over from the sudden cancellation of those titles). It was too soon to tell whether Black Magic and Boys’ Ranch would be successful (Black Magic would be, Boys’ Ranch would fail) but the romance titles still seemed to be very lucrative. Both romance titles had returned to art covers (YL in August and YR in October) but after just two art covers, Young Romance reverted back to photo covers. As for other publishers, the romance glut had finally reached a relative low point and in future months the number of love titles would begin to increase. While the number of romance titles was much lower then at the height of the glut there were still a respectable 45 romance comics books on the racks.

Young Romance #28 (December 1950) “Hot Rod Crowd”, art by Jack Kirby
Once again Jack Kirby was the primary artist during this period with 4 covers, 13 stories and 69 pages. Jack would provide the lead feature for 5 of the issues. The lead stories Kirby did for Young Romance would still be longer then those by any other artists (10 to 12 pages for Kirby compared to a maximum of 9 pages in a story by Bill Draut and another by Leonard Starr). While I was less then enthusiastic about some of the Kirby splashes in the last chapter some of those that Jack provided in these issues are back to his high standards. Kirby continues to use the confessional format for his lead feature splashes. Actually Kirby’s contribution was somewhat greater then I have outlined because as we will see below he provided some layouts as well.
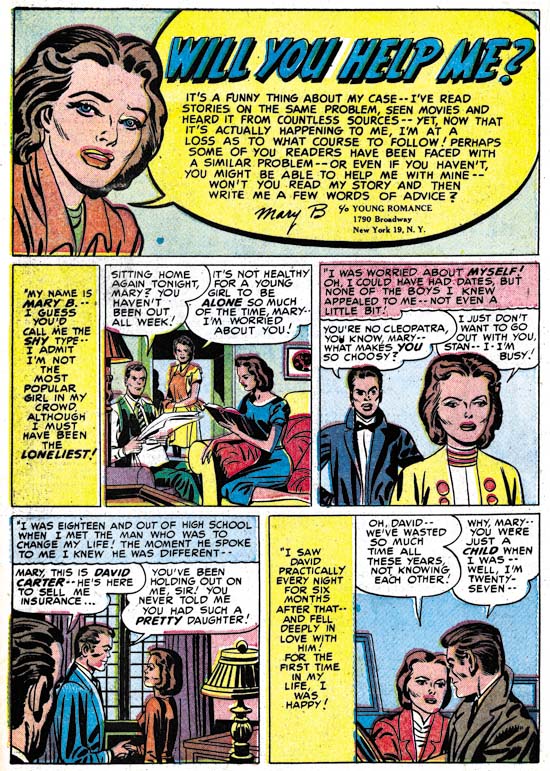
Young Romance #28 (December 1950) “Will You Help Me?”, pencils by Jack Kirby, inks by Bill Draut
It should always be kept in mind when I point out that Kirby was the primary artist that Jack had a substantial advantage over the rest of the studio artists. I am not talking about his greater talent (although that is true) but on the availability of inkers. The Simon and Kirby studio operated very different from say the Marvel studio under Stan Lee during the silver age. Artists working for Simon and Kirby were expected to provide finished art while Stan Lee would typically assign pencils to one artist and afterwards pass the work on to another to do the inking. Most S&K studio artists did their own inking but some made their own arrangements with another artist to do the inking (for instance John Severin would often have Bill Elder ink his work). However Jack Kirby’s pencils were most often inked by others. Joe has described it as an assembly line approach with different hands doing different inking chores. Under that arrangement it is not possible to recognize all the inkers who worked on a particular piece. To make matters worse Kirby inkers never signed their work (that is other then Joe Simon and a Simon and Kirby signature does not necessarily mean Joe inked it). Nonetheless comparing brush techniques on work penciled by Kirby with art drawn as well as inked by other artists allows some of Kirby’s inkers to be identified. For instance the simple eyebrows found on the woman and the cloth folds of the man’s jacket in the last panel of the page above indicate that story had been inked by Bill Draut.

Young Romance #29 (January 1950) “Love Also Ran”, art by Bill Draut
The second most used artist was Bill Draut (7 stories with 53 pages). Previously Draut primarily did horizontal half page splashes but recently has been doing some full page splashes as well. I greatly admire Draut’s art and he has done some nice half page splashes but I must admit that I am underwhelmed by most of his full page romance splashes. They are not bad just not very exciting. That is except for the splash for “Love Also Ran”. Unlike some of his other full pages splashes, here Draut has concentrated on the drama and leaves the background to provide visual interest without overwhelming the image. It is not how Simon and Kirby would have laid it out but it still works just fine.

Young Love #17 (January 1951) “I Saw Him First”, art by Mort Meskin
The third most used romance artist was Mort Meskin (7 stories with 52 pages) although with just one less page then Draut. Generally Meskin provided half pages splashes but for “I Saw Him First” he does a full pages one. Mort does his own take of the confessional splash. What first appears to be a story panel in the corner turns out on reading to be the protagonist introducing the story. And unlike in Simon and Kirby’s confessional splashes, her introduction does not provide the story title. In fact the design of the title is quite unusual for a Simon and Kirby production so perhaps Meskin created the logo as well. It all works out quite well and one wonders why Meskin did not do this sort of thing more often.

Young Love #15 (November 1950) “Lover Boy”, pencils by John Severin, inks by Bill Elder
Kirby, Draut and Meskin did most of the work in these six issues of the romance comics. There are few other artists used and what artists there are supplied limited amounts of material. The next most prolific artist was John Severin who did the art for 4 features but because only one story had more then 2 pages this meant John only did 13 pages of art. John provides his usual quality art but just as typically he seems to be a little out of place in the romance genre. There is not a single kiss to be found in this work.

Young Love #15 (November 1950) “Beauty and The Benefactor”, art by Leonard Starr
Leonard Starr provides a single 9 page romance story in this period. While Starr had not been one of the primary artists for Simon and Kirby productions, he had been a steady presence since April 1949. “Beauty and the Benefactor” will not be the last work by Starr to be used by Joe and Jack but the rest will be more infrequent. The splash shown above is unusual for Leonard who normally did half page splashes and favored vertical ones in particular. This is the only splash Starr did for S&K with a row of floating heads. Further the posses are not typical of Starr either. All of these features are however found in some Simon and Kirby splashes and I am sure that here Starr is working from their layout.

Young Love #15 (November 1950) “Beauty and The Benefactor” page 9, art by Leonard Starr
Starr generally had his own way of laying out story panels. Often he would use tall narrow panels constructed by dividing a row into three panels instead of the normal two and either limiting the page to two rows (thereby making a 2 X 3 panel arrangement instead of the typical 3 X 2, as seen in Chapter 7) or by reducing the vertical dimensions of two of the rows (Chapter 10). While tall narrow panels would not occur on every page they would be found on many. Tall narrow panels are not found at all in “Beauty and The Benefactor” nor were they used in “Hired Wife” published in the previous month (and briefly discussed in the last chapter). Their absence calls for an explanation but unfortunately I can only offer a guess. Since Simon and Kirby provided a layout for the “Beauty and The Benefactor” splash (but not the one for “Hired Wife”) one suggestion might be that they laid out the stories as well. However I do not think that is the case. The page layouts are not a perfect grid of three rows and two columns on all pages but they approximate that arrangement more then was typical for Simon and Kirby. Further the way these stories by Starr are graphically told does not appear to match Kirby’s more cinematic approach.
I would instead propose two, not mutually exclusive, explanations for Starr’s change in panel layouts. One was to speed up the work. With Starr’s previous layouts he could not construct the panels until he had decided what he was going to draw on each page. By adhering to a 3 by 2 panel layout he could construct the horizontal rows for an entire story before actually beginning to draw it and then supply the vertical separation between the two panels in a row as he worked. Simon and Kirby had used this technique on their more complicated panel layouts found in Stuntman and Boys Explorer. The other explanation for Starr’s change in panel layouts may have to do with his desire to break into syndication strips. While the tall narrow panels were very effective in a comic book they would not work well in a syndication strip. Perhaps Starr was consciously changing his working methods to gain experience working in a format more appropriate for syndication work. Starr would in a few years succeed in breaking into syndication with his “Mary Perkins on Stage”.

Young Love #17 (January 1951) “She Loves Too Wisely” page 4, art by unidentified artist
While most of the romance issues covered in this chapter were produced using artists that we have seen often before, there are some artists that seem to be new. I am not sure what to say about “She Loves Too Wisely”. Some of the men in it look like they might have been done by John Severin but not all and none of the women look like his work. Perhaps what makes the art for this story so hard to place is that it would appear from the cinematic approach used in this story that it was drawn from a Simon and Kirby layout. It is even inked in a version of the Studio Style. Note the abstract arch in panel 2 and the frequent shoulder blots (Inking Glossary).

Young Love #17 (January 1951) “Go Home and Grow Up”
Another artist did “Go Home and Grow Up”. This is one of those artist that, although they are not bad, are not as talented as most artists employed by Simon and Kirby.

Young Romance #28 (December 1950) “A Shattered Dream” page 2
Here is the same artist in “A Shattered Dream”. Again not bad but not particularly great either.

Young Romance #28 (December 1950) “A Shattered Dream” page 8
Unlike “Go Home and Grow Up”, not all the art in “A Shattered Dream” is forgettable. Some of it looks very much like Jack Kirby drew it. This is particularly true for page 8. Can there be little doubt about Jack’s hand in the woman in the panel 4? These two pages are the extremes with page 2 showing little evidence of Jack while page 8 looks like almost pure Kirby and the rest of the story falling in between. The layouts of most of the pages look like Kirby’s cinematic approach. If all the pages looked consistently the same I would say that this was the result of some artist’s heavy handed approach to inking Kirby’s pencils. But in a case like this were the art varies I conclude Kirby provided layouts that another artist finished and then inked. Apparently Kirby’s layouts typically were tighter in some spots and loose in others.
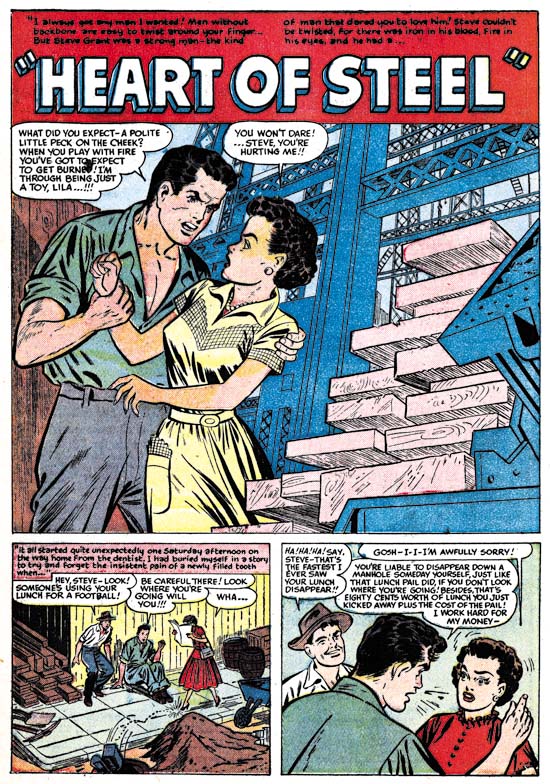
Young Romance #27 (November 1950) “Heart of Steel”
Each publisher had his own house style. This certainly was true with the comics that Simon and Kirby produced. I doubt that Joe and Jack actually told their artists what style to use. I am sure part of the Simon and Kirby house style came from the artists that they selected to work for them. I also believe that Jack Kirby was so well known and respected that he had a great influence on other studio artists. But there are two stories in a single Young Romance issue (YR #27, November 1950) that do not seem to share in the Simon and Kirby house style. In fact they look very much like the very different house style found in Harvey romance comics. This is particularly true of “Heart of Steel”. One of the things that gave Simon and Kirby productions their own unified look was that a single letterer was used (first Howard Ferguson and later Ben Oda). But look at the lettering in the captions above; the lettering is very small in size and uses lower case letters. This is so very different from the lettering used in Simon and Kirby comics that there can be little doubt that it was done by a different letter. Unfortunately I have not had a chance to compare this with Harvey comics from the same period but I have looked at a couple of Hi-School Romance issues from about a year latter and exactly this same lettering is found in them.

Young Romance #27 (November 1950) “My Tormented Heart”
“My Tormented Heart” does not use the same letterer but then again not all Harvey comics that I have seen do. Both stories use the same splash page layout that is found in almost all Harvey romance comics. The title logo and the small circular caption are not typical for Simon and Kirby but can be found in Harvey romance comics. Even the coloring for these two stories has a lighter quality more typical of Harvey then Simon and Kirby productions.
But why would stories with the Harvey house style appear in Young Romance? I think part of explanation can be found in the aftermath of the love glut. While not as big a contributor to the glut as Timely, Fox, Fawcett and Quality, Harvey still had 7 romance titles at the height of the glut. However between April and June of 1950 6 of these titles would either be suspended or cancelled. Only First Love would be continually published during this period. Simon and Kirby had a long history with Al Harvey and had recently starting producing Boys’ Ranch for Harvey. So it would seem that Joe and Jack were picking up some inventory from Harvey. I believe the art was from Harvey and not his artists because it was completed including the lettering and possibly the coloring as well. The question then becomes not so much why Simon and Kirby obtained art from Harvey but rather why they did not pick up more? While Harvey was, like many other publishers, hurt by the love glut it was still obvious that there was good money to be made in romance comics. Harvey would relaunch Hi-School Romance in December, Love Problems and Advice in January and First Romance in June (Love Lessons, Sweet Love and Love Stories of Mary Worth would never resume).
Unfortunately I have no idea who either of the two artists was. I am sure I have seen the artist for “Heart of Steel” in other Harvey romance comics. He provides his women with eyebrows that are reminiscent of Bob Powell. I have heard that Powell often used assistants but I do not believe that is what happened to “Heart of Steel”. Unfortunately it is hard to be sure about anything when it comes to artists working on Harvey’s romance comics. Only Lee Elias, who had a long association with Harvey, ever signed romance art (some covers) so I suspect there was a policy against signatures in Harvey romances. Joe Simon has told me there was such a policy about signing art for Harvey’s humor comics and Joe felt that was why Warren Kramer did not get the recognition that he deserved.
During this period the romance comics were largely made by just three artists; Jack Kirby, Bill Draut and Mort Meskin. While I greatly admire all of those artists I feel that the absence or near absence of Bruno Premiani? and Leonard Starr left a big hole in Young Romance and Young Love. Even Vic Donahue’s presence would have gone a long way to making these more satisfying comic books.
Chapter 1, A New Genre (YR #1 – #4)
Chapter 2, Early Artists (YR #1 – #4)
Chapter 3, The Field No Longer Their’s Alone (YR #5 – #8)
Chapter 4, An Explosion of Romance (YR #9 – #12, YL #1 – #4)
Chapter 5, New Talent (YR #9 – 12, YL #1 – #4)
Chapter 6, Love on the Range (RWR #1 – #7, WL #1 – #6)
Chapter 7, More Love on the Range (RWR #1 – #7, WL #1 – #6)
Chapter 8, Kirby on the Range? (RWR #1 – #7, WL #1 – #6)
Chapter 9, More Romance (YR #13 – #16, YL #5 – #6)
Chapter 10, The Peak of the Love Glut (YR #17 – #20, YL #7 – #8)
Chapter 11, After the Glut (YR #21 – #23, YL #9 – #10)
Chapter 12, A Smaller Studio (YR #24 – #26, YL #12 – #14)
Chapter 13, Romance Bottoms Out (YR #27 – #29, YL #15 – #17)
Chapter 14, The Third Suspect (YR #30 – #32, YL #18 – #20)
Chapter 15, The Action of Romance (YR #33 – #35, YL #21 – #23)
Chapter 16, Someone Old and Someone New (YR #36 – #38, YL #24 – #26)
Chapter 17, The Assistant (YR #39 – #41, YL #27 – #29)
Chapter 18, Meskin Takes Over (YR #42 – #44, YL #30 – #32)
Chapter 19, More Artists (YR #45 – #47, YL #33 – #35)
Chapter 20, Romance Still Matters (YR #48 – #50, YL #36 – #38, YB #1)
Chapter 21, Roussos Messes Up (YR #51 – #53, YL #39 – #41, YB #2 – 3)
Chapter 22, He’s the Man (YR #54 – #56, YL #42 – #44, YB #4)
Chapter 23, New Ways of Doing Things (YR #57 – #59, YL #45 – #47, YB #5 – #6)
Chapter 24, A New Artist (YR #60 – #62, YL #48 – #50, YB #7 – #8)
Chapter 25, More New Faces (YR #63 – #65, YLe #51 – #53, YB #9 – #11)
Chapter 26, Goodbye Jack (YR #66 – #68, YL #54 – #56, YB #12 – #14)
Chapter 27, The Return of Mort (YR #69 – #71, YL #57 – #59, YB #15 – #17)
Chapter 28, A Glut of Artists (YR #72 – #74, YL #60 – #62, YB #18 & #19, IL #1 & #2)
Chapter 29, Trouble Begins (YR #75 – #77, YL #63 – #65, YB #20 – #22, IL #3 – #5)
Chapter 30, Transition (YR #78 – #80, YL #66 – #68, YBs #23 – #25, IL #6, ILY #7)
Chapter 30, Appendix (YB #23)
Chapter 31, Kirby, Kirby and More Kirby (YR #81 – #82, YL #69 – #70, YB #26 – #27)
Chapter 32, The Kirby Beat Goes On (YR #83 – #84, YL #71 – #72, YB #28 – #29)
Chapter 33, End of an Era (YR #85 – #87, YL #73, YB #30, AFL #1)
Chapter 34, A New Prize Title (YR #88 – #91, AFL #2 – #5, PL #1 – #2)
Chapter 35, Settling In ( YR #92 – #94, AFL #6 – #8, PL #3 – #5)
Appendix, J.O. Is Joe Orlando
Chapter 36, More Kirby (YR #95 – #97, AFL #9 – #11, PL #6 – #8)
Chapter 37, Some Surprises (YR #98 – #100, AFL #12 – #14, PL #9 – #11)
Chapter 38, All Things Must End (YR #101 – #103, AFL #15 – #17, PL #12 – #14)


as far as the unknown artists go, I am glad you also saw a slight Severinsk touch in the men of Too Wisely and I also felt a Powell influence in Heart of Steel. On the first I would say it would not surprise me if Kirby himself inked and ‘improved’ a Severin story, together with a studio crew. On the second I agree with your assumption that Simon and Kirby could have bought some leftover stories from te Harvey titles. Even without their own connection witht ha outfit. In later issues they also used leftover material from some of the cancelled Mikeross titles.
Ger,
The Mikeross material came from another comic crash, only one not limited to just romance titles. I am sure in both cases it was the ability to pick up work at bargain prices that promted S&K to use material created for other titles. The deal Joe and Jack had with Prize gave them a percentage of profits for the romance titles but they had to pay all the expenses for creating the art so any such bargains meant less expense from their own pockets.