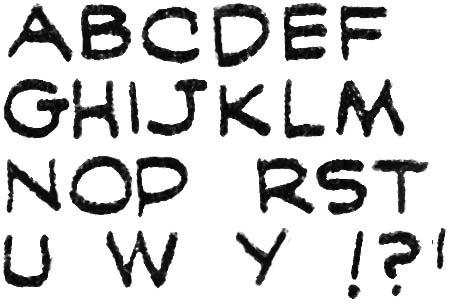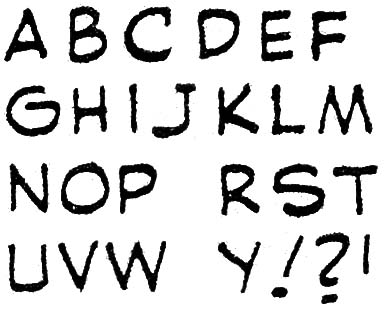Creator credits were pretty much never supplied before the silver age of comics. Therefore we have no good idea who the letterers actually were for a long period of comic book history. In the case of Simon and Kirby we are more fortunate because they have told us who some of the letterers were. It is only a guess but I would not be surprised if over 95% of the lettering on works created by Jack Kirby and Joe Simon up to the breakup of their collaboration can be attributed to just four artists. Actually the overwhelming percentage of it was done by just Howard Ferguson and Ben Oda. However early in their careers both Jack and Joe generally lettered the works that they drew themselves. This was not surprising because typically there was no division of labor in the earliest years of comic books and artists were expected to supply fully inked and lettered art.
For this post I will be writing about the lettering by Jack Kirby. Jack’s earliest work was not in comic books but work intended for publication in newspapers. I suspect much of this was lettered by Jack himself but I am not completely sure. For instance “The Romance of Money” (link 1) was printed as a bank give-a-way in 1937. There are some suggestions that this was Kirby’s writing but it is hard to be sure because some of his more distinctive traits from a few years later are not found.
Kirby also did some lettering in the work that he did for the Iger and Eisner studio. At this point Kirby’s lettering is very much the same as in the examples that I will provide below from a latter period. An example of Kirby lettering from that period can be found in a previous post (see A Brief Pause).
Kirby also did the lettering for the syndication strip Lightin’ and the Lone Rider. Actual I am not sure if this strip was every published in a newspaper but Greg Theakston includes some proofs in his Complete Jack Kirby 1917 – 1940. The Lone Rider strip was included in Famous Funnies however the lettering was redone by some other artist for all the early issues (Famous Funnies #62 to #65, August to December 1939, see Chapter 1 of Early Jack Kirby). Jack’s original lettering was retained for Famous Funnies #72 to #76 (July to November 1940, see Chapter 3 of Early Jack Kirby).

The Blue Beetle (February 1940), letters by Jack Kirby
The earliest samples of Kirby’s own lettering that I will supply come from the Blue Beetle syndication strip that Jack did for Fox Comics in 1940. Others who have previously written about detecting Kirby’s lettering have placed much emphasis on his distinctive ‘U’ with its ends curved inwards in a “horseshoe” shape. Kirby’s ‘U’ is very helpful for detecting Kirby’s lettering but I have also found his ‘G’ helpful as well. Observe the small vertical stoke that drops from the lower end of the letter. The vertical stroke does not always dip below the rest of the letter but even so its straight form can often be detected. Some letters by Kirby are not so distinctive from those used by other letterers but still are useful in cases where the ‘U’ and ‘G’ are not so helpful. In particular are ‘J’ without a cross stroke at the top, ‘M’ with slopping sides, and a ‘Y’ with a diagonal lower portion. Despite the vertical characteristic of Kirby’s alphabet he nonetheless executes his exclamation point at an extreme angle. Not infrequently Kirby fails to connect the strokes that form letters and I provide examples of such a failing for ‘K’ and ‘P’ and the bottom.
For an example of Kirby lettering for the Blue Beetle please see Chapter 2 of Early Jack Kirby.

Prize Comics #8 (January 1941), letters by Jack Kirby
I provide above letters from a somewhat later period taken from the Black Owl story published in Prize Comics #8. It can be seen that little has changed in Kirby’s lettering. In fact most of the differences that can be seen between the two examples I provide are actually not due to some evolution of Kirby style but rather to the wide range of variation that occurred in the lettering of a single story. For example I show from Prize Comics #8 two versions of the letter ‘S’. I also provide two further examples of letters (‘B’ and ‘R’) where Kirby fails to connect the strokes.
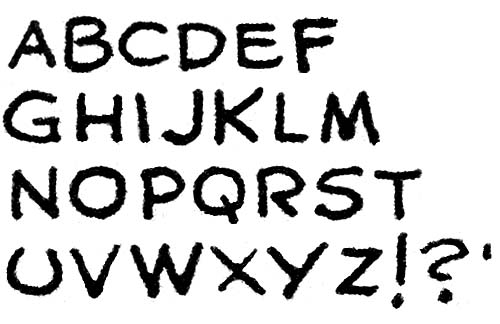
Captain America #2 (April 1941) “Hurricane”, letters by Jack Kirby
My final set of letters by Kirby come from a story that probably was the last published one he ever lettered, “Hurricane” from Captain America #2. Also published in April was “The Underground Empire” from Daring Mystery #7 but that story was probably reworked material originally done earlier for the never published Red Raven Comics #2. Again there is little changed to be observed in Kirby’s lettering. Perhaps the most significant is that Jack now provides a more vertical form to his exclamation points.
Captain America was a big success and Jack Kirby would from then on concentrate on the art and would no longer letter his stories. The period that Kirby did lettering was relatively short and I provide below all the comics that I believe he lettered. However care must be used in some of the cases because Jack’s was not the only hand involved. But I will go into that in more detail later.
Captain America (Timely (Marvel))
1 Mar 1941 10p "Murder, Ltd."
1 Mar 1941 6p "Stories From The Dark Ages"
2 Apr 1941 10p "Hurricane"
Crash (Tem Publishing)
a 1 May 1940 5p "The Solar Legion"
a 2 June 1940 5p "The Solar Legion"
a 3 July 1940 5p "The Solar Legion"
Daring Mystery (Timely (Marvel))
7 Apr 1941 8p "The Underground Empire"
Famous Funnies (Eastern Color)
72 July 1940 2p "Lightnin' and The Lone Rider"- (Kirby lettering page 2)
a 73 Aug 1940 2p "Lightnin' and The Lone Rider"
a 75 Oct 1940 2p "Lightnin' and The Lone Rider"
a 76 Nov 1940 2p "Lightnin' and The Lone Rider"
Jumbo (Fiction House Magazines)
a 1 Sept 1938 4p "The Count of Monte Cristo"
1 Sept 1938 4p "Wilton of the West"- (Kirby letters page 4)
a 2 Oct 1938 4p "The Count of Monte Cristo"
a 2 Oct 1938 4p "The Diary of Dr. Hayward"- (Kirby lettering page 3)
a 2 Oct 1938 4p "Wilton of the West"- (Kirby letters pages 3 & 4)
a 3 Nov 1938 4p "The Diary of Dr. Hayward"
a 3 Nov 1938 4p "Wilton of the West"
Marvel Mystery (Timely)
13 Nov 1940 8p "The Vision"
14 Dec 1940 7p "The Vision"
15 Jan 1941 7p "The Vision"
Mystery Men (Fox)
a 10 May 1940 3p "Wing Turner"
Prize (Prize)
8 Jan 1941 6p "Black Owl"
8 Jan 1941 6p "Ted O'Neill"
Red Raven (Timely (Marvel))
1 Aug 1940 8p "Mercury In The 20th Century"
s 1 Aug 1940 7p "Comet Pierce"
Romance of Money (Natamsha Publishing)
**** 1937 24p ""- (bank give-away)
Science (Fox)
a 4 May 1940 8p "Cosmic Carson
Wow (Fawcett)
1 Spr 1941 7p "Mr. Scarlet"