(Real West Romance #1 – #7, Western Love #1 – #6)
The first issue of Young Romance was cover dated September 1947. The Simon and Kirby modus operandi was adhered to for that new title. That is it was a bimonthly title and initially depended greatly on the drawing talents of Jack Kirby. By all reports Young Romance sold quite well but oddly 17 months would pass before a second title, Young Love, was released. Although surprisingly lengthy, the delay itself was also typical. A new title in the same genre normally was not attempted before an indication of the success of the earlier title was confirmed. The second title followed the other aspects of the Simon and Kirby M.O. as well (that is bimonthly and lots of Kirby). Not only were the names of the two comics very similar, the same distinctive title design was used for both thereby linking the two comics in the minds of their readers. At that point there would be a Simon and Kirby love comic released every month. This situation lasted only two months before Simon and Kirby and their publisher Prize Comics began to act very uncharacteristically. April 1949 saw the release of yet another romance title, Real West Romance. Because of the way comics are produced and distributed, two months was much too short a time to show whether Young Love would be as successful as the earlier Young Romance. Even though Real West Romance was a mixed genre combination of love and western this still seems a rather bold move. Particularly bold considering that another part of the M.O. was abandoned; there was not a lot of Jack Kirby drawing in the new title. A short three months later in July yet another new title was released, Western Love. Again three months was not nearly long enough to actually determine how well Real West Romance sold. Once again Western Love did not showcase that much work drawn by Jack Kirby. Why deviate from standard practice with these new titles? More importantly, why such a commitment to the new subgenre, cowboy love?
I had often pondered about that last question, why cowboy love? Particularly since the new subgenre of western romance was not unique to Simon and Kirby either. July (three months after Real West Romance) saw the release of Romance Trail by DC, and Cowboy Love by Fawcett. These dates are much too close to be explained by one publisher trying to copy a competitor’s success. It was only the recently released book, “Love on the Racks” by Michelle Nolan that gave me the answer. Simon and Kirby came up with the original idea for romance comics by observing how popular romance pulps were. As Nolan writes in her book, western love pulps were a very successful subgenre as well. In fact one title, Ranch Romances, was published from 1924 until 1971, well past the heyday for pulps in general. Since the success that romance pulps enjoyed inspired the lucrative romance comics, would it not be expected that the western love pulps popularity might predict rewards for a comic book version? A reasonable conclusion is that Simon and Kirby believed so.
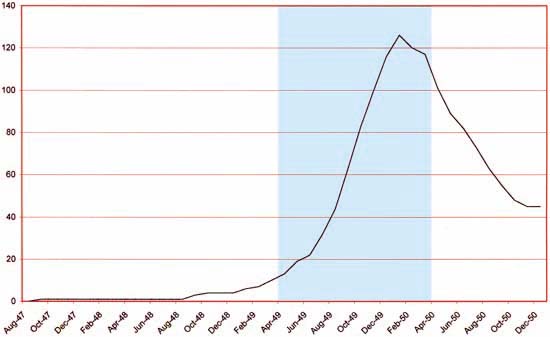
Chart of the number of Romance Titles from September 1947 until December 1950
While reading “Love on the Racks” I thought it might be desirable to come up with a graphical representation for romance comics. I decided to import into a database the information contained from “All the Romance Comics Ever Published (?)” originally compiled by Dan Stevenson. Basically I recorded the range of dates of individual romance titles and used this to graph how many romance titles were out for each month. Despite certain flaws in this method*, the final results greatly exceeded my expectations. Above is an image of the graph from the beginning of romance comics until the end of 1950. Note the delay response of publishers (including Prize) to the success of Young Romance. Also observe how more romance titles were continually added, initially gradually and then dramatically. The peak occurred at January 1950 where there were 126 romance titles out! This is followed by an almost equally dramatic decline in love titles until a low of 45 titles is reached in November 1950. Nolan terms this phenomenon the “love glut”. In those days comics were primarily sold in places like newspaper stands, drug stores and soda shops. Such locations invariably only provided a few racks for comics. Therefore the number of titles of all genres that they sold could be counted in the low dozens. No seller of comic books would be willing to stock 126 romance titles at one time. There simply were too many romance titles out. When publishers realized that they were failing to make the profits they needed a rash of cancellations followed. The biggest publisher of romance titles during the love glut was Timely. In this case Timely’s policy of trying to follow the latest trend probably lost them a lot of money. However Timely’s income was not depended solely on comics and so they seemed to have recovered quickly. The second biggest player in the love glut was Fox. Unlike Timely, Fox Comics did not have much else besides comics to fall back on and the loss from the love glut probably was the cause of Fox going into bankruptcy (again) a few months later.
In the graph that I presented above I have shaded in a light blue the period during which Prize was publishing Real West Romance and Western Love. Unmarked is the starting date for Young Love of February 1949. This suggests a possible scenario. Initially S&K/Prize was satisfied with just publishing Young Romance. However other publishers (starting with Timely and Fox) noticed Young Romance’s success and decided to launch a few romance titles of their own. Seeing that they now had competition, S&K/Prize created Young Love. Having successfully started the romance comic genre, S&K/Prize decided to throw caution to the wind and try to get a jump on the competition for a new subgenre, western romance. It is just a scenario, but it does seem to fit the timeline. The graph indicates that when Real West Romance hit the stands, competition initially was not too bad but would undergo a sudden and substantial increase. Prize was a small publisher and may therefore faced even greater difficulty in getting their new western romance comics onto the stands. Even if that was not the case, the Prize western romance comics faced the same problem with the love glut as all the other publishers. In the end Simon and Kirby’s western romance titles were cancelled like so many other victims of the love glut.
It would not be wise to put all the blame on the failure of Real West Romance and Western Love on the love glut. The romance pulps inspired the creation of love comics but they did not share the same audience. The love pulps were the equivalent of romance books of today, read primarily by women with a range of ages. On the other hand, romance comic books were overwhelmingly purchased by teenage girls. As exclaimed in one house ad by Prize for their own cowboy love comics:
HERE IT IS! ROMANCE WITH ALL THE FURY OF A ROARING SIX-GUN!
LOVE IN THE WIDE OPEN SPACES WHERE THE MOUNTAINS MEET THE SKY… RUGGED MEN AND UNTAMED WOMEN WITH LOVE IN THEIR HEARTS AND GUNS ON THEIR HIPS
This might be very appealing for a more mature reader looking for escapist reading; the sort of reader that kept western romance pulps so popular and long lasting. Teenage girls were undoubtedly looking for something not so much closer to their own lives as closer to their own hoped for future. Few wanted to be cowgirls. The love glut resulted in many cancellations, but romance comics were still popular. The 45 romance titles for November 1950 was still a respectable number of titles. It was also a local low, the number of love comics would increase although never to anything near the peak of the love glut. Romance comics survived the love glut but the western love subgenre did not. Cowboy love disappeared from the comic racks and publishers would not try it again.

Western Love #1 “Weddin’ At Red Rock” (July 1949), art by Jack Kirby
As I mention, Jack Kirby’s contribution to the western romance comics was not nearly as great as it was with previously launches of new titles. There are only a few stories from these cowboy love comics that are what I would call unadulterated Kirby; “Weddin’ At Red Rock” (WL #1), “Mail-Order Romance” (RWR #5), “Dead Ringer” and “Two Can Play The Game” (both from WL #5). These works are easily recognizable as being penciled by Jack. There are a number of other stories which do not show Kirby’s presence so clearly and about which there are differences of opinions. I will be covering those in a couple of weeks. Even including this other work, Kirby does not dominate Real West Romance and Western Love like he previously did Young Romance and Young Love. Jack’s had significantly involvement with only 11 out of a total of 66 stories. As we will see this is not much above the level as some other artists whose work appears in these titles.
Certainly some great stories were created when Kirby’s talent was put to full use. “Weddin’ At Red Rock” is only three pages long but it is a treasure. There are no gun fights, only the threat of their use. Yet the story keeps the reader’s interest. The readers are forewarned about a surprise ending and it is a promise kept, at least it was for me. Despite the lack of typical actions such as gunfights, it is a story very dependant on being a western.

Western Love #5 “Two Can Play The Game” page 4, art by Jack Kirby
“Two Can Play The Game” was another story with a surprise ending, although in this case I saw it coming. Many think of Jack Kirby as primarily an artist of the hero genre. However there is little doubt that Jack did not consider himself as restricted to one genre but as a professional artist willing and capable of tackling any subject. Actually Simon and Kirby pretty much expected all the artists working for them to be able to illustrate any story. Today there are not many fans of romance comics but Kirby’s work in love comics is no less exceptional then anything else he did. Pages like the one above from “Two Can Play the Game” convince me that however scripts were created; Kirby was somehow involved in the process. Invariably it is in the stories that Jack draws that contain the more unusual story presentations. Typically a kiss ends a romance page, or even the story, but here Jack inverts the order at starts with the kiss. Jack Kirby was famous for his graphic command of action, but he sure could put passion into a kiss as well. Having started with an embrace, Kirby then uses an interlude with another man to reveal the woman’s intentions, or lack thereof, before returning to showing her proceeding to her conquest. Would any man resist such an outfit?

Real West Romance #2 (July 1949) “Dead-Game Dude” page 4, art by Bill Draut
We saw in a previous chapter that when Kirby began to provide less for Young Romance and Young Love, it was Bill Draut who took Jack’s place as primary artist. This did not happen with the western love titles. Bill provided 8 stories out of the 66 stories. A respectable number, but by no means did Draut dominate Prize’s cowboy love. The western love subgenre did provide occasions for Bill to draw some action. It was an opportunity that would not repeated until near the end of the Simon and Kirby studio. Draut shows that he has made progress in his depiction of action as compared to what he provided a couple of years previously. Not surprisingly Kirby had a big influence on Draut when it came to a fist fight. This can particularly be seen in the last panel of the page from “Dead-Game Dude” shown above. Bill’s command of exaggerated perspective was not the equal of Kirby, but whose was? I also suspect that Kirby would have placed the flying objects more effectively. Still it is a very dramatic depiction and provides an exciting ending for the page.

Western Love #4 (January 195) “The Girl from Ghost Town”, art by Bruno Premiani?
Above I reproduce the splash page from “The Girl from Ghost Town”. As I discussed in an earlier chapter, the question mark that I apply to the Premiani attribution is because so far I have been unable to find a convincing match with work more securely credited to Bruno. On the other hand nothing I have seen convinces me that the Premiani attribution is incorrect either. I hope someday to resolve this issue at least to my own satisfaction because I really admire this artist. Premiani, if that is whom it is, only worked for Simon and Kirby for a little over a year but during that time he consistently produced nice work. His characters seem to have liveliness to them without the use of exaggerated expressions. His woman are attractive, but in a down to earth way. This is particularly effective in these western stories. What a great cast Premiani presents in the splash panel. They form several groups and truly seem to be interacting. I love the way the can-can dancer performs on the bar for the enjoyment of some customers. Undress her even further and give her audience more modern clothes and it could be a scene in Badda-Bing from the Sopranos. The more things change, the more they stay the same. Premiani provided the art for 6 cowboy romance stories.
Note the small caption “Produced by Simon and Kirby”. This credit first appeared in Real West Romance #3 (August 1949). It would become a staple for the first story in Simon and Kirby comics. After its first appearance, it was only left out in a couple western love comics (RWR #4, RWR #7 and WL #5). It also started showing up in their standard romance comics starting with Young Romance #13 (September 1949). There it would consistently appear with very rare exceptions until Simon and Kirby launched Mainline Publishing in 1954.

Real West Romance #2 “Rough-House Annie” page 5, art by Vic Donahue
We have already encountered Vic Donahue in the pages of Young Romance and Young Love. In those titles Donahue’s contribution was largely limited to very short pieces (2 or 3 pages), at least initially. For the western romance comics Vic got more substantial stories. Generally I choose an image to include in my post that presents the artist most distinctive traits. I must admit my selection here is more for what is being depicted. “Rough-House Annie” is little more then a western “Taming of the Shrew”. I cannot help but believe that this is a case of a lack of understanding by Simon and Kirby of their readership. Would a teenage girl really enjoy the spanking of the lead female? It seems more like a male fantasy to me. Despite the reason for my selecting this page it does show some of Donahue’s characteristics. Note the carefully rendering of the woman’s hair. Also observe the use of fine simple hatching using a pen to provide the shadow cast by a hat in the fifth and sixth panels. Vic typically spots clothing folds as narrow lines. The general absence of picket fence crosshatching (see my Inking Glossary) suggests that for those occasions that it does appear that it was added by another hand.
Real West Romance and Western Love used the talents of a number of artists. Most of these artists were previously discussed in my chapters on Young Romance and Young Love, and others new to this serial post. I have covered a few of them above while leaving others to be discussed next week.
footnote:
* It is easily to imagine other data whose graphs would be better indicators of the relative popularity of romance comics over time. Unfortunately figures for print sizes or copies sold are not available, at least not for all comics over all the period. So with all its shortcomings the number of romance titles has the advantage of being data that has been obtained. There are some weaknesses to graphing this data that I was aware off before I started. I would be treating bimonthlies titles as existing on the racks even for the in-between months. That is not unreasonable because comics were generally kept of the racks for a couple of months. But it does treat monthly and bimonthly with an equality that does not seem correct. Another problem was some the title changes that some comics went through. I made no attempt at distinguishing new titles from title changes. Title changes for monthly comics had no effect, but those for bimonthly would cause a decrement in the title count during the in-between month. Quarterlies were also a problem and not only for the same difficulties discussed above about bimonthlies. Quarterlies are generally not marked by the month, but by the season. I made an arbitrary conversion of seasons to months; Spring, Summer, Fall, Winter were converted to March, June, August and December respectively. Finally some comics had neither marked with the month or the season. Fortunately these were not that common and most of them were IW/SUPER reprints from the 60’s. Despite all these flaws the graph seemed to work out quite well. I suspect the number of titles was always large enough compared to the flaws in the data (the signal to noise ratio) so that the resulting graph is surprisingly smooth.
Chapter 1, A New Genre (YR #1 – #4)
Chapter 2, Early Artists (YR #1 – #4)
Chapter 3, The Field No Longer Their’s Alone (YR #5 – #8)
Chapter 4, An Explosion of Romance (YR #9 – #12, YL #1 – #4)
Chapter 5, New Talent (YR #9 – 12, YL #1 – #4)
Chapter 6, Love on the Range (RWR #1 – #7, WL #1 – #6)
Chapter 7, More Love on the Range (RWR #1 – #7, WL #1 – #6)
Chapter 8, Kirby on the Range? (RWR #1 – #7, WL #1 – #6)
Chapter 9, More Romance (YR #13 – #16, YL #5 – #6)
Chapter 10, The Peak of the Love Glut (YR #17 – #20, YL #7 – #8)
Chapter 11, After the Glut (YR #21 – #23, YL #9 – #10)
Chapter 12, A Smaller Studio (YR #24 – #26, YL #12 – #14)
Chapter 13, Romance Bottoms Out (YR #27 – #29, YL #15 – #17)
Chapter 14, The Third Suspect (YR #30 – #32, YL #18 – #20)
Chapter 15, The Action of Romance (YR #33 – #35, YL #21 – #23)
Chapter 16, Someone Old and Someone New (YR #36 – #38, YL #24 – #26)
Chapter 17, The Assistant (YR #39 – #41, YL #27 – #29)
Chapter 18, Meskin Takes Over (YR #42 – #44, YL #30 – #32)
Chapter 19, More Artists (YR #45 – #47, YL #33 – #35)
Chapter 20, Romance Still Matters (YR #48 – #50, YL #36 – #38, YB #1)
Chapter 21, Roussos Messes Up (YR #51 – #53, YL #39 – #41, YB #2 – 3)
Chapter 22, He’s the Man (YR #54 – #56, YL #42 – #44, YB #4)
Chapter 23, New Ways of Doing Things (YR #57 – #59, YL #45 – #47, YB #5 – #6)
Chapter 24, A New Artist (YR #60 – #62, YL #48 – #50, YB #7 – #8)
Chapter 25, More New Faces (YR #63 – #65, YLe #51 – #53, YB #9 – #11)
Chapter 26, Goodbye Jack (YR #66 – #68, YL #54 – #56, YB #12 – #14)
Chapter 27, The Return of Mort (YR #69 – #71, YL #57 – #59, YB #15 – #17)
Chapter 28, A Glut of Artists (YR #72 – #74, YL #60 – #62, YB #18 & #19, IL #1 & #2)
Chapter 29, Trouble Begins (YR #75 – #77, YL #63 – #65, YB #20 – #22, IL #3 – #5)
Chapter 30, Transition (YR #78 – #80, YL #66 – #68, YBs #23 – #25, IL #6, ILY #7)
Chapter 30, Appendix (YB #23)
Chapter 31, Kirby, Kirby and More Kirby (YR #81 – #82, YL #69 – #70, YB #26 – #27)
Chapter 32, The Kirby Beat Goes On (YR #83 – #84, YL #71 – #72, YB #28 – #29)
Chapter 33, End of an Era (YR #85 – #87, YL #73, YB #30, AFL #1)
Chapter 34, A New Prize Title (YR #88 – #91, AFL #2 – #5, PL #1 – #2)
Chapter 35, Settling In ( YR #92 – #94, AFL #6 – #8, PL #3 – #5)
Appendix, J.O. Is Joe Orlando
Chapter 36, More Kirby (YR #95 – #97, AFL #9 – #11, PL #6 – #8)
Chapter 37, Some Surprises (YR #98 – #100, AFL #12 – #14, PL #9 – #11)
Chapter 38, All Things Must End (YR #101 – #103, AFL #15 – #17, PL #12 – #14)


The the in the splash of The Girl From Ghost Town suggests Leonard Starr to me, but that is probably, because I was expecting to read about him as well. My knowledge of Premiani comes from his Atlas years, when he inked with even more feathering.
Ger,
Have no fear, Leonard Starr will be discussed in the next week’s chapter. As for Premiani, I’ll have to look at some of his Atlas work, but it sounds like he was variable in inking style.
Harry