As I warned previously, I am not going to be the one to break any news about Titan’s Simon & Kirby book projects. But the Jack Kirby Weblog has a post about some new information. Not much but it is better then nothing.
Category Archives: 2008/06
Marvel Reprints or Marvel Recreations?
Dan Best has an interesting post on his blog 20th Century Danny Boy. It is Original Art Stories: Marvel Masterworks Non-Original Artists. In it he discusses Marvel’s policy of re-creating art when the original stats are not available. It sounds like it is a lot more prevalent then I originally believed. I once wrote a post about Marvel’s reprint of the Human Torch #2 (1). In it I used the term re-inked, but in all honesty re-created is a more accurate description.
Admittedly the original comics were printed with a very primitive type of press. I understand why Marvel would want to use stats when available rather then the original comics. But when original stats are not available the idea that a re-creation is superior to restoring from the original comics is just bizarre. Any re-creation no matter how skillfully done is always one artist’s interpretation of another’s work. This is true even if the original artist is used since so many years have passed. This can be misleading to any comic art historian trying to understand the style of the original penciler or inker. What is worse is Marvel does not even provide any indication as to what stories are based on stats and what are re-creations.
The Boys’ Ranch Landscape Swipe

Boys’ Ranch #2 (December 1950) “Lead Will Fly At Sunset”, art by Jack Kirby
In a recent post about Boys’ Ranch I wrote about what is probably the most unusual splash the Jack Kirby ever drew. The reader need not go back to my original post because I include an image of the splash above and here is what I wrote:
Not only did Boys’ Ranch include exceptional pinups, the splash pages are among the best that Jack Kirby did and that is saying a lot. Most of them are full page splashes filled with excitement. However the most unusual splash that Kirby did, not just for Boys’ Ranch but for any Simon and Kirby production, was certainly the one for “Lead Will Fly at Sunset.” Not only does it have no action, it does not even have any characters at all. That is Boys’ Ranch we see below from a distance but there is only the caption to confirm that. What we are provided with is nothing more then a landscape. Well that is a little misleading as this was drawn by Jack Kirby who shows here that he can embody a landscape with interest as well. Partly this is due to the unusual perspective Jack has depicted. In the foreground a steep trail descends to a panoramic vista. The nearby terrain is so rugged that only a few twisted trees have managed to cling to the rocks. With the extensive view it is easy to overlook the most significant inhabitant, a coyote on our left descending via the trail.
But if a reader still wants to go back to my original post here is a link.

Illustration from “The Book of Cowboys” by Holling C. Holling
Kirby scholar and sleuth Tom Morehouse added a comment to my post:
Part of the reason this may stand out is that Jack swiped this particular landscape from The Book of Cowboys by Holling C. Holling (published in 1936).
and he kindly sent a scan of the landscape in question.
Frankly I am not at all surprised that the splash was based on a swipe as it was so unusual. Further that fact that Kirby sometimes used swipes is now too well documented (mostly by Tom) to provide any shock. The equivalent of swiping is a fundamental process in art but only comic art fans use such a derogatory term (swipe is slang for steal). I hasten to add that I believe Tom uses the term for the same reason that I do; the word is so entrenched with comic book fans and requires no explanation. Personally I find cases such as this not a source of embarrassment or condemnation, but as valuable windows into the mind of the creator. Despite my having referred to it as a swipe the splash is truly a Kirby creation and not a mere copy. Compare any detail and it will be seen that Kirby has not followed Holling’s closely. For instance Kirby has only kept one of the distant mountains and even that has been rendered in a manner suggesting that it may be a cloud. This has the effect of making the closer bluffs more dramatic then in Holling’s illustration. Also Kirby has added clumps of trees in the background in places that Holling had left rather featureless.
Although I was not surprised that Kirby swiped this splash I would never have guessed the most important change that Jack made. The most unusual aspect of the comic splash, particularly for an artist like Kirby, was the complete absence of people. It would never have occurred to me that this would not also be found in the original source of the swipe. Yet Holling has foreground figures descending the trail. The most natural expectation would have been that Jack would replace Holling’s figures with Boys’ Ranch members. Unexpectedly Kirby removed Holling’s figures entirely and introduced the lone coyote in their place. It is one of those creative leaps of a great artist that provide awe but can never be truly understood. It seems counter-intuitive, but the removal of all people has made the splash more dramatic.
That the Boys’ Ranch splash was now been shown by Tom Morehouse to be based on a swipe does not diminish it in my eyes. Quite the contrary, seeing how Kirby has used Holling’s book illustration has increased my appreciation for the splash. I may use the term swipe but in reality Jack has not stolen anything.
The Real Reason for the Decline of Comics
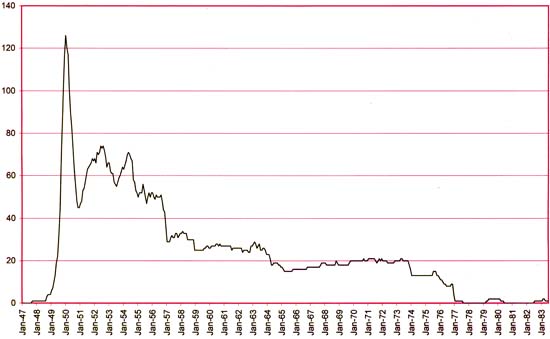
When I reviewed Michelle Nolan’s recent book, “Love on the Racks”, I mentioned that I sometimes had trouble keeping track of the numbers that she would cite to illustrate the ups and downs of romance comics. I therefore resolved to try to make a graphic presentation. I used the data collected by Dan Stevenson found in “All the Romance Comics Ever Published (?)”. As I previously described, what I have done was followed the time during which each romance title appeared and counted up the number of titles that could be expected to be out each month. Bimonthlies were treated as being out in the in-between months (it is not an unreasonable assumption that they would actually stayed on the racks for a couple of months).
Tracking the number of titles provides an indirect indication of the popularity of the romance genre over time. After all if a title sells well enough a publisher is likely to introduce a new one in the same genre, while if sales are poor the title is likely to be cancelled. Thus in such a free market the number of titles is a fair reflection of the popularity of romance comics. There is one important caveat to this statement and that has to do with response time. With comic books it took one to two months to prepare the art, a month for the printing, and another month for the distribution. Comic books were released on assignment and profits were based on the comics actually sold. The publisher would not know how well a particular issue sold for at least a couple of months, if not more. This means that by the time the first indications reached a publisher of how successful a new title was there already may have been as many as four issues released (assuming it is a monthly). Further a publisher might want to give a new title a chance to gain its audience so even further issues might be issued before a poorly selling title might be cancelled.
The lag between release of a new title and the cancellation if it sold poorly is the explanation for the love glut. I previously showed the graph just for the glut itself but the above chart for the entire history of romance comics puts it into a better perspective. The rapidness of the ascent, the height achieved, and the quickness of the decline are unmatched in any other period. Probably unmatched by any other comic book genre as well.
As interesting and distinct as the love glut is revealed in this graph, there are other features that call for explanation. Initially I thought to divide up the chart into three distinct periods. The first period would begin with the love glut and last until early in 1957. The ending for the second period is not as distinct but could be placed between 1963 and early 1965. The final period lasted until late 1977 when the romance genre disappeared. The two small blips (1979/80 and 1982/83) are nothing more then failed revival attempts.
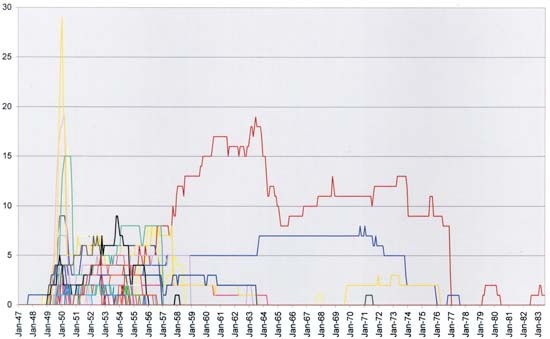
Romance Titles for All Publishers
Different colors are used for the graphs of the individual publishers
I also plotted the number of romance titles for each publisher. Now the reader should not strain themselves trying to understand the ups and downs of the individual publishers. Even with a much larger image then the one I provide above I could never truly distinguish what was going on. This chart does reveal some interesting features. One is how distinct the love glut was even when broken down into the individual publishers. This is because of overzealous actions of four in particular (Timely, Fox, Fawcett and Quality) who combined contributed to about two thirds of the love glut.
Although part of the chart is pure confusion it becomes more understandable from 1957 on. Initially there were a lot of different publishers pursuing the romance comic market but after 1957 their number became drastically reduced. For much of the ending period there were only two or three publishers of romance comics. I will be returning to phenomena below where I will present another way of examining it.
Perhaps the most unusual feature of the chart is the dominance of one publisher from 1957 on. This publisher released romance titles at levels that was only exceeded by Timely, Fox, Fawcett and Quality during the love glut and at one point (1963) was only surpassed by Timely’s peak. Who was the successful publisher? Well it was Charlton. In a free market the number of romance title was supposed to reflect their popularity. Does this mean during the later period Charlton love comics became the most popular of the genre even more successful then any other publisher throughout the history of the romance comics? Not really. Charlton was unique among the romance publishers in that they printed their own comics as well. Charlton would actual save money by keeping the print press continually running. Therefore the company had an incentive to publish comics that had low profits providing they were not actually losing money. Unfortunately that means Charlton is not running under quite the same version of the free market that the other publishers who would be less willing to put effort into titles that produced low profit. Therefore Charlton distorts the picture provided by the first chart.
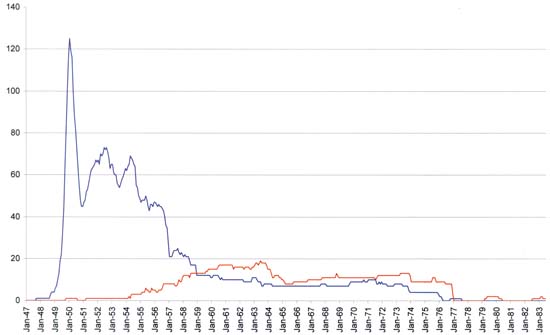
Romance Titles by Charlton and All Other Publishers
Charlton in red, all other publishers in blue
To judge how Charlton was distorting the data, I graphed Charlton separately from all other publishers. This graph shows that what I originally thought was a middle period was actually due to affects of one publisher, Charlton. It might be interesting to determine the meaning of Charlton’s downturn from 1963 to 1965 but that explanation would only enlighten Charlton’s history not to the history of romance comics in general. Therefore I now divide the history of love comics into two periods; an early or flourishing period and a final or waning period. The transition between the two periods is very sharp and that feature is unchanged whether the Charlton data is included or not.
The early period begins with the love glut and last until early in 1957. This is the heyday of romance comics. I would love to call it their golden age but that would only cause confusion as that term is often used among comics in general for an earlier period. It certainly was a good period for publishers of romance comics. Although we can see a lot of fluctuations in the number of titles there were about 50 toward the end of the prime period which is a respectable number for any genre. There are features in this period I would like to understand in particular the two mini-peaks that occurred after the love glut. Were they a similar, but more reduced, version of a phenomenon like the love glut? That is could they have been caused by publishers trying to cash into the popularity of romance comics, albeit with more caution then previously? Or was the popularity of romance comics at that time being influenced by something else as for example the general state of the economy (the trickle down effect)? At this time I have not drawn any conclusions on the matter but the subject deserves more investigation.
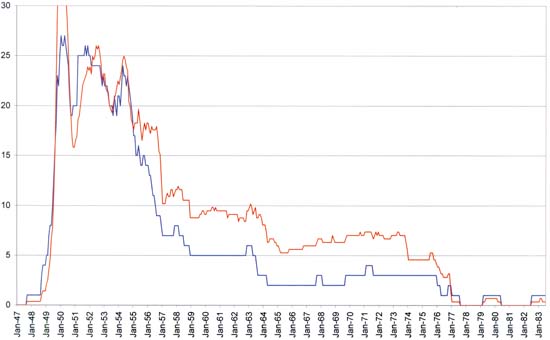
Romance Publishers and Titles
Number of romance publishers in blue, compared with a scaled version of the number of romance titles in red
When I charted the romance titles for each publisher (the second graph) there seemed to be a decline in the number of publishers at approximately the end of the flourishing period. Because that graph was much too confusing to make out the details I decided to chart the number of romance publishers which is shown just above. To help relate the variations in romance publishers to that of romance titles I included the romance titles graph scaled to approximately fit the chart of the romance publishers during the early period. As can be seen there is some good correspondence between the two charts. In particular both graphs show a rapid decline at the end of the flourishing period which terminates at the same February 1957 date. This is not too surprising because a free market affects both the number of publishers as well as the number of titles. Note however that when the number of romance titles was scaled to match the number of publishers during the flourishing period, there are proportionally more titles then publishers during the waning period. One explanation for this divergence is that those publishers who continued to do romance comics were able to increase the number of romance titles they released because of the decrease in the number of competing romance publishers. However remembering how Charlton’s desire to keep their presses running had distorted the romance title graph during the waning period I decided to compare the two graphs with Charlton removed.
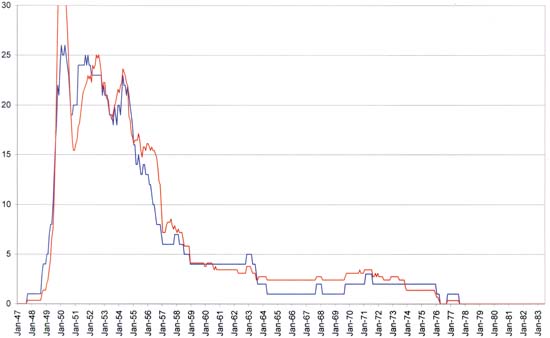
Romance Publishers and Titles Excluding Charlton
Number of romance publishers in blue, compared with a scaled version of the number of romance titles in red
Once Charlton is removed from the picture, the graphs of the number of romance publishers and the scaled version of the number of titles has become remarkably similar. Thus the number of romance publishers and the number of love titles they released both seem to be subject to a free market and both are good indicators of the popularity of love comics.
Either of the charts, including or excluding Charlton, says pretty much the same thing. In the discussion below I will be using the graphs that include Charlton. The most interesting thing about the early period is the rapid decline that ended it. From a local high of 23 romance publishers with 70 titles at June 1954 the number of publishers steadily declined until February 1957 when there were only 7 romance publishers with a total of 29 titles. While the decline in romance publisher was continuous, the decline in titles hovered around the 50 titles mark for much of this period.
It was not just romance, instead there was a decline in comics of all genre at approximately this same time. I have heard two explanations for this. One is that the blame falls on the Comic Code. The idea being that with the heavy censuring of the comic code the quality of the stories declines and many readers lost interest and stopped buying comics. The problem with this explanation is that the Comic Code stamp started appearing on comics on or about March 1955. However the rapid decline had actually started many months before.
Another explanation advanced for the decline of comics of all genres is the rise of televisions. I have two problems with this explanation. One is this presumes that entertainment is a zero sum game. That is the audience for television could not grow without taking readership away from comics. I am not convinced that is true. Secondly the American public did not suddenly buy televisions. TV’s began to appear in the late ’40s however the public’s response was not immediate but was spread out over many years. The end of the prime period occurs over much too short a time to be due to the increased dominance of televisions. So I am unsatisfied with this explanation as well.
Is there any other candidate for the decline that started after June 1954? Well actually there was. June 1954 was the peak but that meant the actual first decline started in July. The dates I have been using are cover dates, which are actually a couple of months later then the true colander date of their release. So the first decline was really in May. April 23 and 23 marked the dates for the Kefauver Senate hearings about the supposed effect of comic books on the youth of America. But the Senate hearings did not come out of the blue; they were part of the response to the public outcry brought on by the book “Seduction of the Innocents” of Dr. Frederick Wertham. There were anti-comic sentiments prior to Wertham’s book, as shown in the recent book “The Ten Cent Plague” by David Hajdu. In fact Wertham had played a part in the earlier anti-comic feelings as well. But using his status as an expert (and without any real scientific evidence) Wertham and his book incited a reaction against comic books greater then ever seen before. As I said his book led to the Kefauver Senate hearings but it had an even more immediate result. There were newsstands and other sellers of comic books that began to refuse comics they considered objectionable. This decrease in sales in turn lead to the failure of the distributor Leading News which in turn lead to the decline of some comic publishers most importantly EC. A later result was the creation of the Comic Code Authority which only made matters worse. All of this started with “Seduction of the Innocent” so the ultimate case of the collapse of comic books can be traced to one supposed expert Dr. Frederick Wertham.
But what if there was no Wertham and “Seduction of the Innocents”? Well such questions can never be answered with complete assurance. Anti-comic sentiments did exist and there were other public figures to promote them. If the previous history of comic criticism was any example then there is no reason to believe that the publishers would ever been faced with much difficulty. What seemed to be needed to bring anti-comic feelings to a significant level was some spokesman like Wirtham. There is no way of knowing whether without Wirtham some other spokesman would have arisen. But it would seem that without Wirtham at least the timing would have been altered and history would have played out differently. How different cannot be guessed.
Another question is that if comics were a free market system, why did not the publishers remaining during the waning period just increase their number of romance titles to bring the number of titles up to levels more closely approximately that of the flourishing period? The answer to that is that not all publishers and their comic titles are alike. This should not be surprising as even today collectors tend to focus on particular comics. Readers were not satisfied to read any comic on the racks but each had their own favorite titles and publishers. When particular publishers disappeared their fans were less satisfied with what remained and less likely to switch to another publisher. The drop in story quality with the Comic Code did not help matters either.
Sky Masters Color Guide, Kirby Kolors?
Ferran Delgado, who as I previously mentioned is working on a Spanish reprint of Sky Masters of the Space Force, has posted an image of a Sky Masters color guide on his blog. There is every reason to believe Jack Kirby did the coloring for the Sky Masters Sunday strips. Therefore the Sunday strips may be the only source to be able to come to a true understanding of Kirby Kolors. It is particularly nice to see an example of the actual color guide. I cannot wait for the final volume (containing the Sundays) of the Spanish Sky Masters reprints to come out.
The Art of Romance, Chapter 8, Kirby on the Range?
(Real West Romance #1 – #7, Western Love #1 – #6)
The theme of this chapter is one that I have touched on before in relationship to some work from Young Romance. Rather then repeat myself over and over again in the examples below I will summarize my argument here. There are five basic ways that some story art might have an incomplete resemblance Jack Kirby’s work; the art may have been done by an artist that was influenced by Kirby; the artist may have swiped from Kirby; Kirby acting as an art editor may have altered another artist’s work; the inker may have deviated from the original pencils by Kirby; or Kirby did layouts that were finished by another penciler/inker. The first three can easily be distinguished from the other two by not being consistently present throughout the story. However distinguishing between the effects of a heavy handed inker or an artist working from Kirby layouts presents more of a problem. In the end it is a judgment call which is probably based in part on how the person making the call feels about the way inkers at the time went about their work. If you believe that inkers working for Simon and Kirby felt that they should impart their own vision on Kirby’s pencils (such as certainly was the case in the silver age) then you are likely attribute stories that do not look like typical Kirby to a heavy handed inker. If, like me, you doubt that an inker would take liberties on tight pencils provided by Kirby (who after all was their boss) then untypical Kirby stories would be better explained as due to an artist working from Kirby layouts. The difference between the two possibilities really is not that great because in these cases the second artist appears to have been the inker as well. Nonetheless I like to make the distinction because there really does seem to be two bodies of work. One group of work is easily identified as by Jack Kirby with all of his characteristic traits no matter who did the inking (the unadulterated Kirby). The other may not always be so readily identified and has unusual traits (unusual at least for Kirby).
I remember that during the silver age Kirby was sometimes listed as having provided layouts while another artist would get the credit for the penciling or finishing. I believe this is just as unfair as the credit Jack sometimes got for plotting while another (Stan Lee) would be credit with the writing. Plotting a story would normally be considered part of writing it just as laying out a story would generally be included in the drawing of a story. Separating plotting from writing or layouts from pencils is fundamentally unfair. In Jack Kirby’s case it is particularly egregious because some of his margin notes ended up in actual dialog and also some of his layouts would be quite tightly rendered in places. Therefore in cases where Jack provided layouts I prefer to credit the pencils to both Jack and the other artist. Unfortunately I have never been able to identify who the finishing artists were.

Real Western Romance #1 (April 1949) “Heart Rustler”, art by Jack Kirby and unidentified artist
The Jack Kirby Checklist cites “Heart Rustler” as being inked, but not penciled, by Jack Kirby. Simon and Kirby’s business was not so much creating comic books as producing them. So it is easy to imagine circumstances where Jack Kirby could be called on to ink someone else’s pencils. I do not know about the reader, but I would love to see how Kirby would ink another artist. So I look at stories like “Heart Rustler” with much interest. However when I examined this story I was disappointed, it was clearly not inked by Jack. Yes there are some places that exhibit some features of Studio style inking. There are some abstract shadows in each panel that are created using a very blunt brush (see my Inking Glossary for explanations of the terms I use to describe inking techniques). Those in the splash panel and first story panel could even be described as having an arced edge. It is probable that Jack or Joe added them. More important are the spotting that is done in a way that Kirby would not have done it. The man blocked out in blue on the left edge of the splash panel has a hat casting a shadow formed by simple hatching; I have never seen Kirby do that. It may be a little hard to make out in the image I supplied but the lower legs of the woman in the same splash panel are shadowed with nearly vertical lines; again this is not an inking technique that Jack used. None of the clothing folds look like Jack’s brush. In fact the shoulder of the woman in the first story panel has a couple of odd blunt spots; one of which is attached to a then line as if it was a leaf on a drooping stem. Kirby would sometimes use similar blots on the edge of a limb as a way of indicating a shadow but he never placed them isolated as done by this inker. Similar problems can be found throughout the story. So I repeat Jack Kirby did not ink this story other then some possible touch ups.
Was the attribution found in the Jack Kirby Checklist just completely unreasonable? No, I think I can understand how it came to be. Look at the face of the woman in the splash. She seems to me to have a very Kirby look to her. Kirby’s hand is a bit harder to see on the rest of the page although I feel it can be seen in the armed gunman in the splash panel. I also believe I can spot Kirby’s touch in the other pages of the story. Further the entire story seems to be laid out in a manner typical for Jack Kirby. I suspect that source of the inking attribution in the Jack Kirby Checklist noted the Kirby look to the story and assumed that it was achieved by Jack inking the piece. Since the brush work itself shows that Kirby was not the inker another explanation must be advanced. The explanation I would give is that Kirby did the layouts for this story. It is apparent that when Jack did layouts the pencils would be tighter in some parts (like the face of the woman in the splash) while other places it would be rougher. Another artist would then tighten up the work and then ink it or perhaps tighten it up while inking.

Real Western Romance #3 (August 1949) “Our Love Wore Six-Guns”, art by Jack Kirby and unidentified artist
Another story identified by the Jack Kirby Checklist as inked but not drawn by Jack Kirby is “Our Love Wore Six-Guns”. Here is a case where the inking is actually done in a manner even further from that used by Kirby then in “Heart Rustler”. Nothing looks like Studio style inking. The clothing folds are typically long and narrow very unlike what Jack was doing at this time. It may be less obvious in “Our Love Wore Six-Guns” then in “Heart Rustler” but there are some faces that look like they had the Kirby touch; for instance the woman in the page’s last panel. These Kirby-like portions occur too frequently throughout the story to be explained as either swiping by the artist or art editing by Jack. The man is just as consistently un-Kirby like in my opinion. I find it hard to believe that an inker would have produced the man’s face in this way had he been inking over tight pencils by Jack. The story layout does seem to have consistently been done in a way appropriate for Kirby. So my conclusion is once again Jack provided layouts and another artist finished and inked them. The inking style used in this story does not match that for “Heart Rustler” so I believe different artists were used for the two stories.

Western Love #2 (September 1949) “Kathy and the Merchant” page 4, art by Jack Kirby and unidentified artist
To be honest I am not very impressed with either of the two artists who worked on the Kirby layouts for the two stories I discussed above. Because of the low quality of the work usually found on Kirby layouts, I believe the layouts were generally provided when Simon and Kirby felt it was necessary to employ the use of artists of lesser talent, perhaps even studio assistants. However there are exceptions such as “Kathy and the Merchant”. The group of men in panels 2 to 4 is, in my opinion, nicely done. I also do not think their higher quality was due to tighter pencils. To my eyes they have a blend of Kirby and non-Kirby elements. Page 4 is typical of the story so swiping or editing can be eliminated as explanations. I can understand if others believe that Jack did the pencils that were just inked by another, but I prefer to think that Jack supplied layouts not tight pencils. I will say that the Jack Kirby Checklist credits Joe Simon with the inking but I feel that is clearly wrong. The brushwork is much too fine in this story to be the work of Joe.

Real Western Romance #4 (October 1949) “Perfect Cowboy” page 4, art by Jack Kirby and unidentified artist
I think “Perfect Cowboy” also falls into the category of Kirby layouts. The splash may have been particularly tighter and was not inked by the same artist as the rest of the story. The story inking is very interesting. At a glance it appears to be Studio style brushwork. Certainly that was what the inker was attempting. But this is not Joe Simon’s inking as suggested by some. The picket fence crosshatching only superficially resembles Jack or Joe’s brush. The pickets have a distinct pointed end and progressively widen through most of their length unlike the more uniform width found in Kirby, Simon or even Meskin’s use of the Studio style. I am not sure I would call it true picket fence, but simple crosshatching is applied to the dust cloud in panel 3 which is unlike anything I have seen by an inker working in the Studio style. However the most unique technique of this inker is his applying of picket fence crosshatching to the hair of the woman as best seen in the last two panels of this page. The pickets are placed in the same direction as would be expected for the hair and therefore the rails are at odds to the flow of the hair. This is all meant to suggest shadows formed on the lower parts of the waves and curls but the result is decidedly unnatural looking. I do not remember seeing this spotting of hair ever being repeated in Simon and Kirby productions.

Real Western Romance #7 “Loves of a Navajo Princess”, art by Jack Kirby and unidentified artist
The final story that I will cover is a tough call. The two Indians in the splash panel were clearly done by Jack Kirby. The Studio style inking that the left part of the panel shows almost convinced me that this was an example of Jack as art editor fixing up the splash. However close examination showed that the same inking style was used on the rest of the splash. Actually the entire story is done in Studio style inking; picket fence crosshatching, drop strings, abstract arc shadows, the works. In fact the inking job is truly well done but it just does not look like Kirby’s brush. The biggest giveaway is the cloth folds which have a distinct tendency for elongated folds in some places and irregular blots in others. Nowhere else does the art look quite as pure Kirby as the splash but there are more then enough places that have Jack’s touch to convince me that it was his layouts. But like I said it is a tough call and I am not sure many will agree with me, certainly the Jack Kirby Checklist does not.
This chapter concludes the western romance section of The Art of Romance. I have added to my sidebar checklists for Real West Romance and Western Love. Cowboy love was an interesting experiment but it just was not a very successful one. The love glut resulted in the cancellation of a lot of romance comics including the western subgenre. However it would not be correct to blame the demise of the western romance on the love glut. Despite all the cancelled love titles there must have been enough profits during the love glut to convince at least the major publishers to continue to produce a significant number of titles. In contrast none of the publishers decided to continue the western romance titles. The effects of the love glut on the romances that Simon and Kirby produced for Prize was very divergent. Real West Romance and Western Love must not have sold well as they were cancelled just after the peak of the love glut. Young Romance and Young Love not only seemed to weather the love glut but to flourish. But that will be discussed in future chapters of The Art of Romance.
Chapter 1, A New Genre (YR #1 – #4)
Chapter 2, Early Artists (YR #1 – #4)
Chapter 3, The Field No Longer Their’s Alone (YR #5 – #8)
Chapter 4, An Explosion of Romance (YR #9 – #12, YL #1 – #4)
Chapter 5, New Talent (YR #9 – 12, YL #1 – #4)
Chapter 6, Love on the Range (RWR #1 – #7, WL #1 – #6)
Chapter 7, More Love on the Range (RWR #1 – #7, WL #1 – #6)
Chapter 8, Kirby on the Range? (RWR #1 – #7, WL #1 – #6)
Chapter 9, More Romance (YR #13 – #16, YL #5 – #6)
Chapter 10, The Peak of the Love Glut (YR #17 – #20, YL #7 – #8)
Chapter 11, After the Glut (YR #21 – #23, YL #9 – #10)
Chapter 12, A Smaller Studio (YR #24 – #26, YL #12 – #14)
Chapter 13, Romance Bottoms Out (YR #27 – #29, YL #15 – #17)
Chapter 14, The Third Suspect (YR #30 – #32, YL #18 – #20)
Chapter 15, The Action of Romance (YR #33 – #35, YL #21 – #23)
Chapter 16, Someone Old and Someone New (YR #36 – #38, YL #24 – #26)
Chapter 17, The Assistant (YR #39 – #41, YL #27 – #29)
Chapter 18, Meskin Takes Over (YR #42 – #44, YL #30 – #32)
Chapter 19, More Artists (YR #45 – #47, YL #33 – #35)
Chapter 20, Romance Still Matters (YR #48 – #50, YL #36 – #38, YB #1)
Chapter 21, Roussos Messes Up (YR #51 – #53, YL #39 – #41, YB #2 – 3)
Chapter 22, He’s the Man (YR #54 – #56, YL #42 – #44, YB #4)
Chapter 23, New Ways of Doing Things (YR #57 – #59, YL #45 – #47, YB #5 – #6)
Chapter 24, A New Artist (YR #60 – #62, YL #48 – #50, YB #7 – #8)
Chapter 25, More New Faces (YR #63 – #65, YLe #51 – #53, YB #9 – #11)
Chapter 26, Goodbye Jack (YR #66 – #68, YL #54 – #56, YB #12 – #14)
Chapter 27, The Return of Mort (YR #69 – #71, YL #57 – #59, YB #15 – #17)
Chapter 28, A Glut of Artists (YR #72 – #74, YL #60 – #62, YB #18 & #19, IL #1 & #2)
Chapter 29, Trouble Begins (YR #75 – #77, YL #63 – #65, YB #20 – #22, IL #3 – #5)
Chapter 30, Transition (YR #78 – #80, YL #66 – #68, YBs #23 – #25, IL #6, ILY #7)
Chapter 30, Appendix (YB #23)
Chapter 31, Kirby, Kirby and More Kirby (YR #81 – #82, YL #69 – #70, YB #26 – #27)
Chapter 32, The Kirby Beat Goes On (YR #83 – #84, YL #71 – #72, YB #28 – #29)
Chapter 33, End of an Era (YR #85 – #87, YL #73, YB #30, AFL #1)
Chapter 34, A New Prize Title (YR #88 – #91, AFL #2 – #5, PL #1 – #2)
Chapter 35, Settling In ( YR #92 – #94, AFL #6 – #8, PL #3 – #5)
Appendix, J.O. Is Joe Orlando
Chapter 36, More Kirby (YR #95 – #97, AFL #9 – #11, PL #6 – #8)
Chapter 37, Some Surprises (YR #98 – #100, AFL #12 – #14, PL #9 – #11)
Chapter 38, All Things Must End (YR #101 – #103, AFL #15 – #17, PL #12 – #14)
The Art of Romance, Chapter 7, More Love on the Range
(Real West Romance #1 – #7, Western Love #1 – #6)

Real Western Romance #6 (February 1950) “I’m Goin’ a’ Cortin’ Ella Mae” page 7, art Leonard Starr
Leonard Starr is most known for his syndication strip Mary Perkins on Stage. He had a long career but I suspect the work that he did in romance comics probably was more important in relationship to his success with the newspaper strip then what he did in any other genre. Starr was an important artist for Real West Romance and Western Love. No single artist dominated these titles but Leonard did more work then any other artist. Not all his work was signed, but I believe he provided 10 out of the 66 stories. Now in my last week’s post I mentioned that Kirby provided significant contributions to 11 stories. I hope to be able to show in my next post what Jack’s contribution was for these stories. For now let me say that most of the stories were not fully the work of Kirby and are dependant greatly on the efforts of other artists. Therefore I give Starr more credit for his efforts in these western love titles then even Jack Kirby.
In my choice of an example of Leonard Starr’s work I decided not to use one that emphasized his talents in romance (but you can see an example of that in Chapter 5). Instead I picked one that gives a good idea of his skill at graphic story telling. In this sequence we see the progression of Marsh’s decision to defy the male members of the Bates family, his arrival ready for action, and the tense confrontation. However in the final panel the action from an unexpected quarter provides a surprise ending for the page. It really is a nice example of Starr’s own graphic story telling. I feel that this page would almost certainly have been handled differently by Jack Kirby. I am sure that Jack would have put more humor in the final sequence by revealing the brooms handler. The point is not that Jack was a better artist (he was) but that I feel that this indicates that Kirby was not involved in laying out this story. This is not a new observation on my part and I am sure that I will repeat in often in the future. I simply have not found evidence to support the contentions of a few individuals that Jack Kirby provided layouts for many of the artists that worked for the Simon and Kirby studio. That is not to say Jack did not do layouts, but I will leave an explanation of what might seem like a contradiction for the next post.
Leonard Starr can present somewhat of a challenge in recognizing his unsigned work. His drawing can vary somewhat from panel to panel. For instance generally his women have a child-like or elfin look. But then in another panel the woman’s face will have a more normal beauty. I am not sure, but I suspect this sort of variation can be explained by Starr’s occasional use of swipes. If Leonard was doing a bit of swiping at this point in his career, and I want to emphasize I do not know this for sure, it was not from Jack Kirby. Starr already seems to have progressed to his own style of comic art and did not seem to fall under Kirby’s spell.
One final comment about Leonard Starr’s work in the Simon and Kirby western romances concerns his panel layouts. The most common page layout among the various studio artists was three rows with two panels per row. Now this was by no means invariable but it did dominate. Leonard Starr would use that panel layout as well but he had a distinct tendency to break the rows into three panels per row. He would sometimes go further and vertically compress two rows so that the other row would have distinctly tall and narrow panels. Starr would at times go even further yet and organize the page, as in the example above, into two rows of three panels per row so that all the panels would have the narrow format. Other studio artists would occasionally use narrow panels, even Kirby, but none of them as frequently as Leonard Starr.

Real Western Romance #1 (April 1949) “Wild Hoses and Ornery Gals”, art by Al Eadeh and John Belfi
I have previously written about the team of Al Eadeh and Jon Belfi in Chapter 5. They had a small but important presence in the early Young Romance and Young Love issues. So far the above story is the only one that I can credit to Eadeh and Belfi in the western romance comics. It is a safe bet because it is signed. Most artists that worked for Simon and Kirby were expected to illustrate any category of story. So the fact that I have attributed 6 stories to Eadeh and Belfi from YR and YL but only one from RWR or WL is suspicious. Either they were exceptions and were predominately assigned standard romance work, or some of the work I have credited to them in YR and YL was incorrect, or there is more work to be found in RWR and WL. There are still a number of cowboy love stories that remain unaccredited but so far I do no find any of them convincing examples of Eadeh and Belfi’s work. As I wrote before, Al and John were, like most artists who worked for Simon and Kirby, talented but were not what I would call exceptional.

Western Love #1 “The Tonto Express” (July 1949), art by George Gregg
George Gregg is one of my newer additions to identified Simon and Kirby artists. In the past I have either overlooked his signature or been unable to correctly read it. To the two works I spotted in Chapter 5 (Young Love #4 and Justice Traps the Guilty #17) I have now been able to add another “Fortune In Furs” from JTTG #19 (October 1950). The newly identified piece is another example of a signature I had previously seen but until recently was not able to correctly read. This last work is important because in it Gregg depicts some of the male characters with more complex eyebrows. Perhaps this reflects an influence from Jack Kirby who frequently provides expressive eyebrows. The manner the eyebrows are drawn in JTTG #19 has a pretty good match in “The Tonto Express” and that is one of the reasons I assigned that unsigned work to George. It is gratifying to be able to attribute more art to Gregg and I suspect I will find even more, but I am getting the impression that he only did a little work for Joe and Jack.

Western Love #5 “Lilly’s Last Stand” (March 1950), art by Mort Meskin
December 1949 marked the return of Mort Meskin in Young Romance #16 and Real West Romance #5. Mort had previously provided some work to Simon and Kirby but as part of a team with Jerry Robinson. Robinson and Meskin really did not do a lot of work for S&K but what they did was at a time that when only a small group of artists were supplying art for Young Romance. With his return as a solo artist, Mort would quickly become one of the essential members of the Simon and Kirby studio, or as I like to think of it as one of the usual suspects. Although I use the term “studio artist” most who produced art for Simon and Kirby did not actually work in the studio. Mort was one of the exceptions. As Joe Simon describes in “The Comic Book Makers”, Meskin initially had trouble executing his assignments. Simon was well aware of how talented Mort really was, so first Joe tried patience and when that was not enough he asked Mort to work in the studio. There Joe realized that Mort had a terror of the blank page, and so Joe would have somebody just marks the pages up. Some have claimed that this meant Jack was doing the layouts for Mort, but Joe insists that is not true; the pencils were nothing more then abstract marks. Having overcome his artist block, Mort went on to become a productive member. So productive, that his output exceeding Jack Kirby’s during some periods. I have long believed that Meskin inked his own work. During a conversation with Joe Simon I was told how inking was done in the studio using an assortment of people, “like a factory”. But then Joe paused, and added “except for Mort Meskin, he did all his own inking”. It is nice to have such confirmation.
What an unusual, but effective, composition Meskin provides for the splash panel of “Lilly’s Last Stand”. It depicts Lilly, acting as the sheriff, breaking up a barroom brawl. Normally a fight would be given center stage, but here Mort has placed the fighters in the background. Well, calling it background is a little misleading as all the characters share a rather narrow depth that Meskin makes look natural by using a high viewpoint. There is no true background as nothing is shown beyond the fighters. One of the fighters has been knocked down to the ground while the other advances on him with menace. Across the empty space stands the second fighter’s true opponent, Sheriff Lilly. Lilly is so much in control of the situation that she casually rests one leg on a fallen barstool. We only see the back of the heads of the on looking crowd, except for one that turns to seemingly comment to another observer but really to the reader. By his statement he is Lilly’s boyfriend and thus Meskin has presented a roll reversal of the sexes, the theme of the story. During his years with S&K Mort had a distinct preference for a two thirds of a page splashes. One reason appears to have been that it allowed him to play off the splash panel with the first couple of story panels. That is true here where the story panel shows Lilly in a very feminine dress in contrast to the sheriff outfit. Interestingly Mort provides another level to the contrast. I describe the dress as feminine but the high collar effectively hides her female anatomy while the plunging neckline of her sheriff outfit neckline reveals them. Was this a suggestion that the feminine roll was actually sexually repressive? Perhaps I am reading too much into it, but that is one of the greatest pleasures reading these stories some 50 plus years later.

Western Love #1 (July 1949) “A Gal, A Guy and a Gelding”, art by Manny Stallman
Another artist we have not encountered before in The Art of Romance is Manny Stallman. Had I been writing about Simon and Kirby’s crime comics, we would have seen Stallman’s work earlier because art signed by him began appearing there starting with Headline #22 (December 1948). The attribution of “A Gal, A Guy and a Gelding” is considered tentative and is based on the general style. The fact that it is the only unsigned work credited to Manny in my database suggests that further investigation should reveal more works by him (most artists working for S&K did not sign everything they did). I would not be surprised if crops up again when this serial post returns to discussing Young Romance and Young Love, but I have not found any more of his works in Real West Romance or Western Love. Currently my database only has 8 works by Stallman with the one in WL #1 being the last.
Despite the western theme, most stories from the western love comics are typical romance stories. There is however a greater emphasis on action found in RWR and WL as compared to YR and YL. “A Gal, A Guy and a Gelding” illustrates that quite well. Stallman shows he can handle the action well enough but he clearly did not learn how to depict a fight from Jack Kirby. Jack discovered quite early in his career that the best way to present a person slugged was to have him project toward the reader; Manny has the man fall away from us. Further the slugger seems to be unnaturally leaning towards us. Still there is no question about what is going on. Since this is first and foremost a romance story it has a typical romantic ending. Panel 5 shows that Manny was better then most of the artists in RWR and WL in providing a romantic image, I wonder why Manny was not used more often in YR or YL? As I previously said, most of these cowboy love stories are really romances and as such they typically end with a kiss. I have to laugh about the ending for “A Gal, A Guy and a Gelding” where instead there is a mutual embrace of a horse. (In all fairness, this was probably determined by the script writer).

Real Western Romance #3 (August 1949) “The Cowgirl and the Sheepherder”, art by John Severin and John Belfi
I left for last another artist not previously encountered in The Art of Romance. John Severin would pencil 10 stories for the Prize cowboy romance comics, the same number as Leonard Starr. I give Starr the credit for being the most prolific of the western romance artists because one of Severin’s pieces was a single page. Still Severin was one of the dominate artists, and he also did work for the crime and standard romances comics as well. Here in “The Cowgirl and the Sheepherder” he is inked by John Belfi. We had previously seen Belfi as teamed up with Al Eadeh. John Belfi was primarily an inker but he did occasionally do pencils. In fact just a couple of months previously he penciled a story for Justice Traps the Guilty. As far as I know this is the only S&K studio story where Belfi inked Severin. I thought it might be interesting to include a sample for comparison with Severin’s normal inker.

Real Western Romance #6 (February 1950) “Six Gun Serenade”, art by John Severin and Will Elder
Although this is my first occasion to discuss Severin in The Art of Romance, I did write about some of his much later work for Joe Simon. Therefore I may as well confess up front that I am not a fan of John Severin; I find his style too dry. However when studying comic art history it is important to separate personal tastes from the study itself. I may not care that much for Severin, but that does not change the fact that he was an important artist. I will also say that Joe Simon does not share my view; Joe greatly admires John Severin. On the occasion of the recent death of Will Elder, Joe commented how talented Severin and Elder were as a team and how each would become great in their own particular art form.
It is with Will Elder that John Severin is most often teamed up with in Simon and Kirby productions. Severin and Elder are an exception among the S&K studio artists in that their work was not evenly distributed among genre. Typically studio artists were expected to be able to work on any type of story. However Severin and Elder did very few standard romance stories while as stated above they did a good number of the western love subgenre. They also did some crime stories, but by this time the Prize crime titles were no longer being produced by Simon and Kirby. It was in western genre that Severin and Elder did the most work. My knowledge of Prize Comics Western (also not produced by S&K) is not adequate, but it does seem that Severin and Elder appeared there before showing up in other Prize titles. Further John and Will became regular artists for Prize Comics Western for a number of years.
Severin’s pencils can most easily be recognized by the very wide and square jaw that he usually gave to men. The reader can see a good example of this in the first panel of the page from “Six Gun Serenade” that I provide above. However I chose this particular page to show that John Severin was not always so dry or limited to serious westerns. Here we get a chance to see a more humorous Severin. His rendition of Phil mimicking Slim’s singing in the third art panel is just marvelous. Even better is Phil’s reaction in the sixth art panel after being slugged by Slim. Unquestionably, Severin had the ability to go beyond his normally dry manner when the occasion called for it. Unfortunately there was one thing that John did not seem very successful at and that is romance. If not for the text in the captions the reader of “Six Gun Serenade” would have no idea the couple in the last panel were in love. John Severin just did not seem to have the romantic touch. That may have been fine for these western love stories, but it may explain why Severin and Elder did so little work for Young Romance and Young Love. Still I must say that although I generally do not care for Severin’s work, there are occasions like “Six Gun Serenade” where he just bowls me over.

Western Love #4 (January 1950) “Six Gun Serenade”, art by John Severin and Will Elder, along with Jack Kirby
With all the comics that Joe Simon and Jack Kirby produced over the years, it is understandable that occasionally a story title would be repeated. Even so it is a bit surprising that “Six Gun Serenade” would be reused as a title within just a month. That is not why I have chosen to include the image above. The real reason is the figure of the wounded Dirk in the splash panel. It is clearly the work of Jack Kirby. The inking of the figure and the surrounding wall also appears to have been done by Jack. The rest of the splash and the two story panels were just as clearly done by John Severin and Will Elder. This is one of those cases of Kirby stepping in as art editor. It may not be too surprising that Severin’s original version was not considered good enough. A comparison of the figure in the splash with the one in the first panel that has just about the same pose suggests what may have been the problem.
There are a number of works in Real West Romance and Western Love that I have not been able to provide an attribution. Some are clearly done by the same artist and so I hope that eventually I should be able to figure who that artist was. There are also some that look like Jack Kirby was involved. These stories and the nature of Jack’s involvement will be discussed in next week’s conclusion to the western romance titles.
Chapter 1, A New Genre (YR #1 – #4)
Chapter 2, Early Artists (YR #1 – #4)
Chapter 3, The Field No Longer Their’s Alone (YR #5 – #8)
Chapter 4, An Explosion of Romance (YR #9 – #12, YL #1 – #4)
Chapter 5, New Talent (YR #9 – 12, YL #1 – #4)
Chapter 6, Love on the Range (RWR #1 – #7, WL #1 – #6)
Chapter 7, More Love on the Range (RWR #1 – #7, WL #1 – #6)
Chapter 8, Kirby on the Range? (RWR #1 – #7, WL #1 – #6)
Chapter 9, More Romance (YR #13 – #16, YL #5 – #6)
Chapter 10, The Peak of the Love Glut (YR #17 – #20, YL #7 – #8)
Chapter 11, After the Glut (YR #21 – #23, YL #9 – #10)
Chapter 12, A Smaller Studio (YR #24 – #26, YL #12 – #14)
Chapter 13, Romance Bottoms Out (YR #27 – #29, YL #15 – #17)
Chapter 14, The Third Suspect (YR #30 – #32, YL #18 – #20)
Chapter 15, The Action of Romance (YR #33 – #35, YL #21 – #23)
Chapter 16, Someone Old and Someone New (YR #36 – #38, YL #24 – #26)
Chapter 17, The Assistant (YR #39 – #41, YL #27 – #29)
Chapter 18, Meskin Takes Over (YR #42 – #44, YL #30 – #32)
Chapter 19, More Artists (YR #45 – #47, YL #33 – #35)
Chapter 20, Romance Still Matters (YR #48 – #50, YL #36 – #38, YB #1)
Chapter 21, Roussos Messes Up (YR #51 – #53, YL #39 – #41, YB #2 – 3)
Chapter 22, He’s the Man (YR #54 – #56, YL #42 – #44, YB #4)
Chapter 23, New Ways of Doing Things (YR #57 – #59, YL #45 – #47, YB #5 – #6)
Chapter 24, A New Artist (YR #60 – #62, YL #48 – #50, YB #7 – #8)
Chapter 25, More New Faces (YR #63 – #65, YLe #51 – #53, YB #9 – #11)
Chapter 26, Goodbye Jack (YR #66 – #68, YL #54 – #56, YB #12 – #14)
Chapter 27, The Return of Mort (YR #69 – #71, YL #57 – #59, YB #15 – #17)
Chapter 28, A Glut of Artists (YR #72 – #74, YL #60 – #62, YB #18 & #19, IL #1 & #2)
Chapter 29, Trouble Begins (YR #75 – #77, YL #63 – #65, YB #20 – #22, IL #3 – #5)
Chapter 30, Transition (YR #78 – #80, YL #66 – #68, YBs #23 – #25, IL #6, ILY #7)
Chapter 30, Appendix (YB #23)
Chapter 31, Kirby, Kirby and More Kirby (YR #81 – #82, YL #69 – #70, YB #26 – #27)
Chapter 32, The Kirby Beat Goes On (YR #83 – #84, YL #71 – #72, YB #28 – #29)
Chapter 33, End of an Era (YR #85 – #87, YL #73, YB #30, AFL #1)
Chapter 34, A New Prize Title (YR #88 – #91, AFL #2 – #5, PL #1 – #2)
Chapter 35, Settling In ( YR #92 – #94, AFL #6 – #8, PL #3 – #5)
Appendix, J.O. Is Joe Orlando
Chapter 36, More Kirby (YR #95 – #97, AFL #9 – #11, PL #6 – #8)
Chapter 37, Some Surprises (YR #98 – #100, AFL #12 – #14, PL #9 – #11)
Chapter 38, All Things Must End (YR #101 – #103, AFL #15 – #17, PL #12 – #14)
Please Excuse Me While I Ramble On
I am in a funny situation. Since I am involved in the Titan book deal you would think this blog would be a great source for all sorts of information about the project. Actually that is far from the case. For instance I was scooped on the Titan press release. Not only that but one investigator reported on the deal months ago (and no I will not say who he was and how he did it). It is not that I do not know what is going on. Often I do (however not always) but it is not my position to pass that information along. All news about this project has come from Titan in the past that will continue to be the case in the future. I will pass information along only when it becomes official. I suspect that this blog will not be the first to report project news.
Some people have offered various types of help. It is certainly gratifying to see how willing people are to further not just this project but any that is related to Jack Kirby and Joe Simon. Unfortunately I cannot respond to those offers, at least now.
Although I cannot talk much about the project I do not think it would be wrong for me to comment about the people. I am greatly pleased about the commitment I have seen. Titan wants these volumes to be as good as possible. I do not think fans will be pleased with the books when they are released, I think they will be thrilled. I believe that is what everyone on this projects wants.
Let me wrap this up by expanding my subject matter beyond the Titan book project and talk a bit about recognition. In the past Jack Kirby did not get the credit that he should have. Sure Kirby fans knew how important Jack was, but the public at large did not have a clue. You would have thought that the blockbuster movies based on characters Kirby co-created would have changed the public’s perception (or more accurately lack thereof). But it did not happen. I think that now it is changing and I credit Mark Evanier’s book “Jack Kirby: King of Comics” with being pivotal for that change. However Jack Kirby was not the only one who did not get the recognition that he deserved, Joe Simon did not get the proper credit either. This was particularly depressing to me because some of this neglect originated from people who should have known better. The general attitude was that in the Simon and Kirby collaboration all the art tasks were handled by Jack and Joe only did the business end and some inking. I feel that this is changing as well. More and more I am hearing comments about Joe’s importance. I wish I could say that this blog was instrumental to this change but I know that simply is not the case. My readership is much too small for my efforts to have been the cause. If I am right about the shift in recognition for both Jack Kirby and Joe Simon, the future should be very exciting times for their fans.
Timely and the Romance Glut
In Chapter 6 of “The Art of Romance” I presented a graph of romance titles that vividly depicted what Michelle Nolan described in her book “Love on the Racks” as the love glut. I mentioned that the two greatest participators in this rush to produce romance comics were Timely and Fox Comics. The reward received by Fox Comics for their zealous jump into love comics seems to have been the bankruptcy that terminated the company a few months afterwards. Timely obviously survived, but I wondered if more could be determined about what effect the love glut had on them? This time I turned to Atlas Tales (what a great site). I used their search engine to provide all the titles between August 1948 and June 1951. I then entered that information into a database and segregated the titles to romance and non-romance.
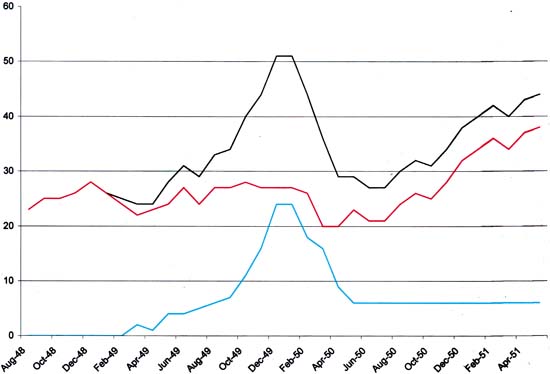
Chart of Timely Titles (Romance titles in blue, non-Romance titles in red, and the combined titles in black).
The resulting graph is not perfectly smooth but it still is revealing. It looks to me that when romance titles were first introduced they took the place of other genre comics as shown by the small dip. However the non-romance genres quickly recovered to their pre-romance levels while more and more romance titles were added. Finally a maximum of 24 romance titles were reached, just 3 titles short of all the other genres combined. This was followed by the crash. Now the cancellation of romance titles is expected but note that the non-romance titles also dipped in February 1950. This suggests that the glut resulted in enough of a financial loss that it impacted other titles as well. As I mentioned in Chapter 6 a low of romance titles was achieved in November of 1950 after which the number of romance titles began to climb although never reaching anything near the levels at the peak of the glut. Timely did not participate in this resurgence and instead maintained a steady level of 6 romance titles for the period covered. The non-romance Timely titles quickly returned to their pre-glut levels (by September 1950) and then continued to levels even higher then before the glut. Whatever financial loss Timely suffered was short lived. I wondered if the even higher levels that Timely achieved after the love glut could have been at the expense of other publishers, like Fox, who were not able to recover so quickly?
New Volume of Sky Masters of the Space Force
I have recently obtained a copy of “Sky Masters of the Space Force” Libro 1. This is the first of what should become a three volume set. The restoration of the newspaper strips were made by Ferran Delgado, who has his own blog. I am of the habit of periodically visiting his blog just to look at the beautiful images of comic art that he provides. Unfortunately I have a serious problem with his blog and this “Sky Masters” book as well, no hablo Espanol. I took three years of Spanish in high school but I am afraid I passed only because I was the quietest person in the class.
Still I am particularly looking forward to the volume containing the Sky Master Sunday strips. Ferran has posted some of his restorations and one of them has also appeared in Mark Evanier’s “Jack Kirby: King of Comics”. These restorations are nothing short of drop dead gorgeous. Ferran is taking great care to faithfully restore the original colors of the printed version. Readers of my blog should not be surprised to find that I feel recoloring was one of the greatest banes of earlier reprints of material drawn by Jack Kirby. This particularly egregious in the case of Sky Master because there is every reason to believe that Kirby did the original color guides himself. It is much more likely that work done for the Sky Master in the late fifties could lead an understanding of the true nature of Kirby Kolors then any of the work that Jack did in the ’80s or ’90s.
So congratulations to Ferran Delgado for successfully bringing the first volume of Sky Masters to print. I know it required a lot of work, but the result certainly justifies the effort.