
Bullseye #7 (August 1955), pencils and inks by Jack Kirby
The bulls-eye pattern returns to the cover image for Bullseye #7. The overlapping figures creates an interesting design where the background figures are carefully framed by the foreground ones. It is always little more than guesswork when trying to credit who did what in the Simon and Kirby collaboration, in this case I suspect that Jack did the layout since this sort of careful arrangement of figures was often found in the work he produced later when working without Joe. While it is an interesting composition, it is not at all clear what is being depicted. All three individuals appear to be aiming their arrows at different targets, so it does not appear to be a shooting contest. Bullseye’s smile would be out of place for a combat usage. In any case why would a cavalry soldier be using a bow and arrow? While Simon and Kirby covers generally can be decoded to reveal a story, the cover for Bullseye #7 seems meant to be nothing more than an compelling image.
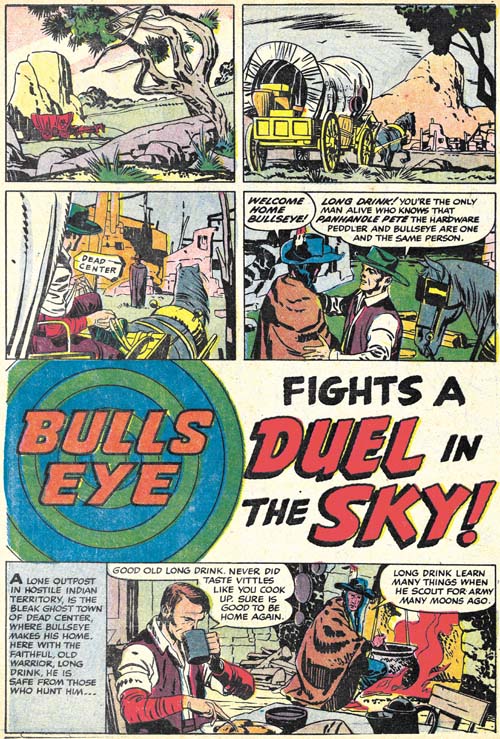
Bullseye #7 (August 1955) “Duel in the Sky”, pencils and inks by Jack Kirby
The first story, “Duel in the Sky”, has an unusual opening; no splash panel and the title occurs below two panel tiers and above another story panel. Kirby has used splash-less stories before but this one is special. The first three panels have no text and show nothing more than Bullseye’s alter-ego traveling over a western landscape. Simon and Kirby usually try to fill their stories with as much as possible so allocating the three panels used in this introduction is quite special. Obviously the introduction was considered worth it but perhaps the splash was sacrificed to make room for it (it is the only Bullseye story without a splash). This introduction shows Bullseye returning to Dead Center, his birthplace, to visit his friend Long Drink. Normally Bullseye traveled about; only in one other story (“The Ghosts of Dead Center”, Bullseye #3) does Bullseye visit Dead Center. This sort of reference to his past was unusual at that time where continuity was pretty much neglected in comic books.
Kirby always had a penchant for technology so I suspect it was his idea to include balloons in this story. The use of such a technology at that period is not unrealistic. During the civil war an attempt was made to use hot air balloons for observation. Unfortunately the balloons became a target and at least one was shot down. In any case the balloons adds interest to another Simon and Kirby masterpiece. It does not hurt either that the story ends with another fantastic Kirby fight.

Bullseye #7 (August 1955) “The Flaming Arrow”, pencils and inks by Jack Kirby
While “Duel in the Sky” has a perfectly acceptable ending, “The Flaming Arrow” picks up from there with Bullseye going off to prevent an errant balloon from falling into the hands of Mexican bandits. It is a short but rather nice piece that ends with Bullseye returning to visit Long Drink once again, the last page being a bookend to the first page of “Duel in the Sky”. In fact the same three panels, with slightly different cropping, that showed Bullseye traveling show up again.

Bullseye #7 (August 1955) “The Stolen Rain God” page 5, pencils and inks by Jack Kirby
The next and what would turn out to be the final Bullseye story, “The Stolen Rain God” opens with a double page splash. I have discussed this piece of art previously in my yet to be completed serial post (The Wide Angle Scream, Almost an Afterthought). Simon and Kirby had a long history of the use of these wide splashes but there were only two created during the Mainline/Charlton period and this was the only one actually published on two pages (the other from Win A Prize #1 was rotated and printed on a single page, see the previous link).
Since I have already posted on the splash page, here I include an image of page 5. It serves as a reminder that while action was the key component of many Simon and Kirby productions, and Bullseye in particular, humor also played an important roll. The very physical humor found in the last three panels is very typical of Kirby.

Bullseye #7 (August 1955) “Fightin’ Mad”, pencils by Jack Kirby, inks by Joe Simon?
This issues ends with a Sheriff Shorty feature drawn by Kirby. This makes Bullseye #7 the only issue from that title entirely drawn by Jack. Normally this would make issue #7 a very special comic. The Sheriff Shorty story is special alright but for the wrong reason. It is a rare example of a clunker drawn by Kirby. The action scenes are uncharacteristically poorly executed and this cannot be blamed on the inker. Further the humor does not quite work. Hey everybody can have a bad day.
None of the Mainline titles lasted very long at Charlton, they were usually terminated after two issues (except for Foxhole which lasted for a third issue but that last issue appears to have been produced by Charlton without any involvement from Simon and Kirby). Bullseye was not an exception and issue #7 would be the last. In my opinion, all the Mainline titles were special but for Kirby fans Bullseye would be the most important. None of the other Mainline titles has anywhere near as much of Kirby drawn material. The only comic from this period that does was Fighting American. Which makes it especially unfortunate that Bullseye has never been reprinted. With the resurgence of interest in Kirby, hopefully that will change in the not too distant future.

































































