(February 1953 – April 1953: Young Romance #54 – #56, Young Love #42 – #44, Young Brides #4)
Number of Romance Titles 1947 – 1954 (the period covered in this chapter is shaded in blue)
I must admit we have entered the period of Simon and Kirby’s romance production that I find the least interesting. This is somewhat unfair because most of the artists used were doing good work. Part of the problem is that while the art was still fine it was largely done by artists we have seen for a number of years. Another contributing factor was that Simon and Kirby were having greater difficulties in coming up with new plots. There are still some stories that are real gems, but they just were not as frequent as previously. I had considered devoting longer periods of time for each chapter but I feel that by keeping on the current three month pace allows me to present more examples of work by artists that are much too overlooked today.
I have remarked in the last couple of chapters of The Art of Romance and The Little Shop of Horrors that Jack Kirby had become more productive after a long period where S&K comics depended more on other artists. While Kirby had become more prominent he still had not returned to the really dominant status he had in earlier years. That is until this period where Jack provides 62 pages of art. This is well above the second place artist who was John Prentice with 46 pages. Third place was taken by Bill Draut (38 pages) and fourth by Mort Meskin (31 pages). These four artists provide almost all the art for this period with Al Eadeh(?) drawing a single story, an unidentified artist contributing two stories and another artist, probably a studio assistant, doing three single page features. Completely absent are two artist that were pretty common presence in previous chapters; George Roussos and Bob McCarty(?).

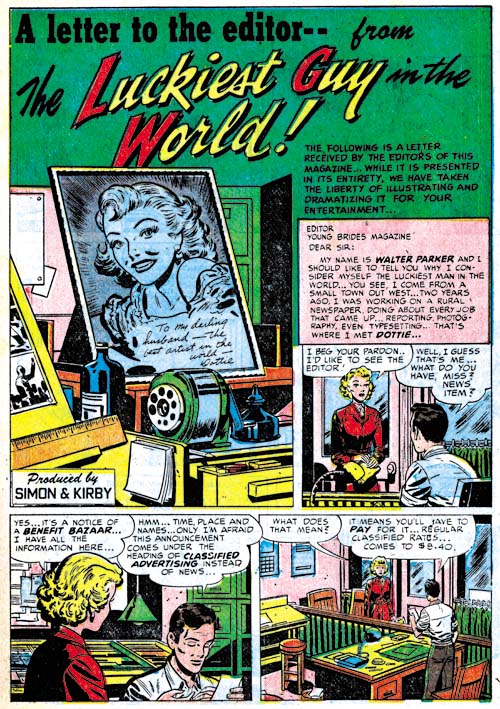
Young Love #43 (March 1953) “Teen-Aged Widow”, art by Jack Kirby
Kirby is not only back in terms of quantity of art, much of it consists of rather nice material. Four of the seven featured stories were done by Jack and one of them, “Teen-Aged Widow”, even returns to a longer length (12 pages) that had previously been typical for Kirby. The splash page for “Teen-Aged Widow” is rather nice. It is a great example of a confessional splash, what young reader of the day could have resisted such a story. Tears do not play so important a part in Simon and Kirby romances as they did in comics produced by others during the silver age. But those tears are very appropriate here. Note how the small sculpture piece in the foreground repeats the protagonists reclining posture. One odd thing is the small size of the books in the foreground. I doubt that this was meant to be taken literally but was just a consequence of the limited space available.

Young Love #43 (March 1953) “Girl Friday”, art by John Prentice
The work by John Prentice during this period is an exception to my lack of great enthusiasm for this period of S&K romance. This is probably due the relatively late arrival of Prentice into the Simon and Kirby production having started just two years previously. Even Meskin has been around longer (three years) while Kirby and Draut have been around since the beginning (six years ago). While Meskin has only been around one more year then Prentice he produced a lot of more work. John was generally not the most productive of the studio artists which is all the more reason to be pleasantly surprised by the amount of work he did during the period covered in this chapter.
The splash for “Girl Friday” is another of those by Prentice that eliminates the normal panel borders. Perhaps my fondness for this effect has caused me to include in my posts enough examples to mislead my readers into thinking this was Prentice’s typical approach. Actually borderless splash panels were pretty uncommon for Prentice however he did use this format more often than other studio artists.

Young Brides #4 (April 1953) “Here Cries the Bride”, art by Bill Draut
Bill Draut’s romance art has not changed very much over the years. Joe Simon has remarked to me a number of times how reliable Draut was, a true professional. Bill graphically told his story in a clear manner with enough variations in viewpoints to keep the reader’s interest. Probably none of the studio artists other than Kirby made as effective use of background details in his splashes. These details probably do not mean much aesthetically but are quite important in capturing part of the story in the splash. While Draut’s style did not evolve much during the period he worked for Simon and Kirby it would undergo large changes afterwards. Although Draut’s art became more acceptable to silver age publishers unfortunately in my opinion the changes to his style were detrimental to his art.

Young Brides #4 (April 1953) “Under 21”, art by Mort Meskin
I feel that the work Mort Meskin did during this period was on a whole not as good as his earlier efforts. That is not to say there were not an exceptions and “Under 21” was certainly one of those. What a great splash, perhaps Meskin’s best effort for a feature story. The wistful pose of the young lady wonderfully captures the mode of the story. The scandal suggested censored newspaper clipping was sure to attract the reader. Meskin’s placing the protagonist on a small town front porch is unexpected but rather effective. The quality of Meskin’s inking had recently been rather sporadic but here the pen and brush are fully under Mort’s competent command. Fortunately none of Meskin’s work for this chapter was inked by George Roussos. I have to admit that I find the inking by Roussos of pencils done by Meskin or Kirby to have been at best unfortunate and at worst disasters.

Young Love #44 (April 1953) “What’s Mine Is Yours”, art by Al Eadeh?
I do not have much to say about the single story questionably attributed to Al Eadeh but I did want to include another example of his work.

Young Romance #55 (March 1953) “Heartless”, art by unidentified artist
Two stories (“Heartless” and “The Other Woman”) by an unidentified artist occur in the same Young Romance issue. He is certainly not among my favorites but he is competent artist nonetheless.
Chapter 1, A New Genre (YR #1 – #4)
Chapter 2, Early Artists (YR #1 – #4)
Chapter 3, The Field No Longer Their’s Alone (YR #5 – #8)
Chapter 4, An Explosion of Romance (YR #9 – #12, YL #1 – #4)
Chapter 5, New Talent (YR #9 – 12, YL #1 – #4)
Chapter 6, Love on the Range (RWR #1 – #7, WL #1 – #6)
Chapter 7, More Love on the Range (RWR #1 – #7, WL #1 – #6)
Chapter 8, Kirby on the Range? (RWR #1 – #7, WL #1 – #6)
Chapter 9, More Romance (YR #13 – #16, YL #5 – #6)
Chapter 10, The Peak of the Love Glut (YR #17 – #20, YL #7 – #8)
Chapter 11, After the Glut (YR #21 – #23, YL #9 – #10)
Chapter 12, A Smaller Studio (YR #24 – #26, YL #12 – #14)
Chapter 13, Romance Bottoms Out (YR #27 – #29, YL #15 – #17)
Chapter 14, The Third Suspect (YR #30 – #32, YL #18 – #20)
Chapter 15, The Action of Romance (YR #33 – #35, YL #21 – #23)
Chapter 16, Someone Old and Someone New (YR #36 – #38, YL #24 – #26)
Chapter 17, The Assistant (YR #39 – #41, YL #27 – #29)
Chapter 18, Meskin Takes Over (YR #42 – #44, YL #30 – #32)
Chapter 19, More Artists (YR #45 – #47, YL #33 – #35)
Chapter 20, Romance Still Matters (YR #48 – #50, YL #36 – #38, YB #1)
Chapter 21, Roussos Messes Up (YR #51 – #53, YL #39 – #41, YB #2 – 3)
Chapter 22, He’s the Man (YR #54 – #56, YL #42 – #44, YB #4)
Chapter 23, New Ways of Doing Things (YR #57 – #59, YL #45 – #47, YB #5 – #6)
Chapter 24, A New Artist (YR #60 – #62, YL #48 – #50, YB #7 – #8)
Chapter 25, More New Faces (YR #63 – #65, YLe #51 – #53, YB #9 – #11)
Chapter 26, Goodbye Jack (YR #66 – #68, YL #54 – #56, YB #12 – #14)
Chapter 27, The Return of Mort (YR #69 – #71, YL #57 – #59, YB #15 – #17)
Chapter 28, A Glut of Artists (YR #72 – #74, YL #60 – #62, YB #18 & #19, IL #1 & #2)
Chapter 29, Trouble Begins (YR #75 – #77, YL #63 – #65, YB #20 – #22, IL #3 – #5)
Chapter 30, Transition (YR #78 – #80, YL #66 – #68, YBs #23 – #25, IL #6, ILY #7)
Chapter 30, Appendix (YB #23)
Chapter 31, Kirby, Kirby and More Kirby (YR #81 – #82, YL #69 – #70, YB #26 – #27)
Chapter 32, The Kirby Beat Goes On (YR #83 – #84, YL #71 – #72, YB #28 – #29)
Chapter 33, End of an Era (YR #85 – #87, YL #73, YB #30, AFL #1)
Chapter 34, A New Prize Title (YR #88 – #91, AFL #2 – #5, PL #1 – #2)
Chapter 35, Settling In ( YR #92 – #94, AFL #6 – #8, PL #3 – #5)
Appendix, J.O. Is Joe Orlando
Chapter 36, More Kirby (YR #95 – #97, AFL #9 – #11, PL #6 – #8)
Chapter 37, Some Surprises (YR #98 – #100, AFL #12 – #14, PL #9 – #11)
Chapter 38, All Things Must End (YR #101 – #103, AFL #15 – #17, PL #12 – #14)
































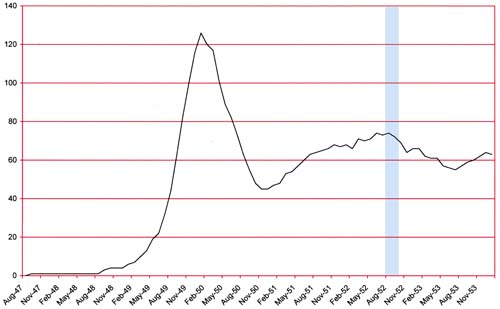










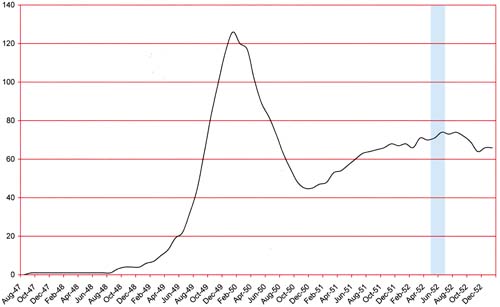 Number of Romance Titles 1947 – 1953 (the period covered in this chapter is shaded in blue)
Number of Romance Titles 1947 – 1953 (the period covered in this chapter is shaded in blue)