(July – December 1955: Young Romance #78 – #80, Young Love #66 – #68, Young Brides #23 – #25, In Love #6, I Love You #7)
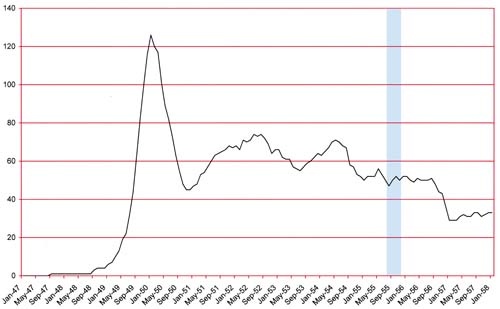
Number of Romance titles 1947 – 1958 (the period covered in this chapter is shaded in blue)
This continued to be troubling times for comic book publishers. Although the graph of the number of romance titles shows a relatively flat period, in fact the number of publishers of romance comics continued to decline (The Real Reason for the Decline of Comics). Simon and Kirby’s publishing venture (Mainline) ended in the period covered in the last chapter (Chapter 29) but they had transferred their titles to Charlton for publication. Even that did not save the Simon and Kirby titles for long. The Mainline romance title, In Love, ended at Charlton with issue #6 (July 1955).
There was an important change in the rostrum of artists supplying work for the Simon and Kirby romance comics, Jack Kirby was back providing art for the Prize love titles. During the period covered in this chapter Kirby would draw 47 pages of art followed by Joanquin Albistur (33 pages); Bill Draut (29 pages); Mort Meskin (16 pages); Bob McCarty, Ann Brewster and Marvin Stein were all tied (13 pages); Bill Benulis (7 pages); and John Prentice, Al Gordon and Lazurus (6 pages each). There were still a lot of relatively new and unidentified artists (58 pages). Kirby had returned to being the primary artists after a period of relative inactivity. However Kirby’s return came toward the end of this period but before that return the things were pretty much like it was during the last chapter.

Young Romance #78 (August 1955) “Army Nurse”, art by Joaquin Albistur
As noted above, Jo Albistur was the second most productive artists during this period. Albistur worked for Simon and Kirby for a little over a single year but during that time he was an important contributor to both Prize and Mainline titles and even appeared in Win A Prize (Charlton). However Albistur was never used for Black Magic, probably because that was not his strongest forte. Apparently Jo did a little work for another comic publisher (which I find much too dry) and appeared in Humorama as well (but too risque to be shown in this blog). Despite his short appearance, Jo Albistur is one of my favorite artist that worked for Simon and Kirby. He would last appear in Young Romance #79 (October 1955).
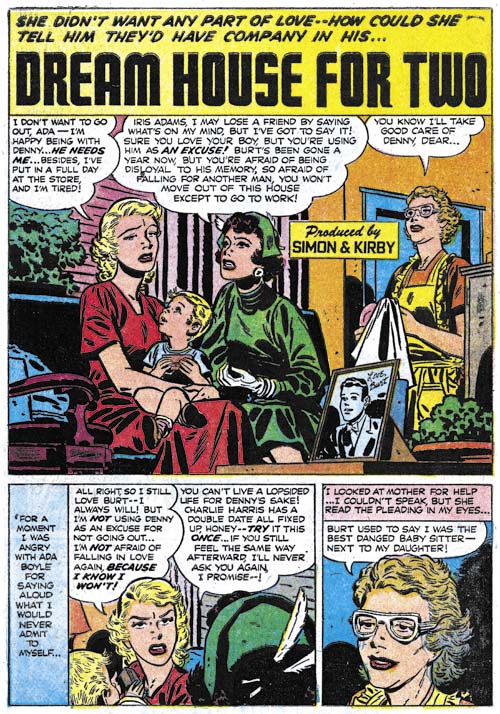
Young Romance #78 (August 1955) “Dream House for Two”, art by Bill Draut
Bill Draut could be described as the work horse for the Simon and Kirby studio. More than any other artists, Bill consistently produced a significant amount of art for all Simon and Kirby productions. He was also the longest running artist working for the studio having started on some features used in Stuntman and Boy Explorers titles that Joe and Jack launched after returning from military service. Draut met Joe Simon in Washington DC when both were still in the service (Bill in the Marines and Joe in the Coast Guard). It was Joe who convinced Bill to try working as a comic book artist. As far as I know the only other publisher that Draut worked for up to now was Harvey Comics. I do not know if Bill independently met Al Harvey or whether this connections was through Joe as well. Unlike the other artists in this post, we will see a little more work by Bill but not for a few chapters.

Young Love #68 (December 1955) “No One To Marry”, pencils by Mort Meskin
Mort Meskin did not work for as long as Bill Draut but he certainly created more art than anyone other than Kirby and there were periods that he even out produced Jack. Mort has been a very over looked artist. This is partly because his work during the war has largely not be reprinted. Further during much of the fifties he was over shadowed by Kirby. Jack was THE best comic book artist but that does not mean all other artists are not worthy of recognition. The work that Meskin is most well know for was for DC horror titles during the late 50’s. Mort tried to adapt his art to look more like the DC studio style making that perhaps his lest artistically successful period. I intend to include in this serial post Prize romance titles not produced by Joe and Jack so we will see a little more work by Meskin. But Mort would never again work for Simon and Kirby.

Young Romance #79 (October 1955) “A Vision of Beauty”, art by John Prentice
John Prentice was the last of what I refer to as the usual suspects (along with Draut and Meskin). While he would appear in some Harvey titles that I believe were edited by Joe Simon, he also would not be used in any more Simon and Kirby productions nor in any of the other Prize romance titles. He would do a little work for DC but unlike Draut and Meskin, his later career was actually quite successful. Prentice was called upon to take over the Rip Kirby syndication strip after the untimely death of Alex Raymond. I cannot think of an artist better suited to this task. I am not saying Prentice was as good an artist as Raymond but John was so influenced by Alex that he was able to take the strip over without a too obvious style change. I am a great admirer of the work Prentice did for Joe and Jack but I believe his work on Rip Kirby was even greater. Unfortunately I doubt we will see Prentice’s Rip Kirby reprinted (at least in my life time) but I do intend to post about it someday.

Young Love #68 (December 1955) “Language of Love”, art by Bob McCarty
Bob McCarty appeared often enough in Simon and Kirby productions that perhaps I should also include him in the “usual suspects. I have to admit that for sometime I credited work by McCarty from 1954 and 1955 to John Prentice. For some reason McCarty’s style changed to one more like Prentice’s at this time. This maybe nothing more than their being mutually influenced by Alex Raymond’s Rip Kirby strip. However the resemblance on occasion is so close that a more personal connection is possible.

Young Romance #79 (October 1955) “Poor Marcie”, art by Ann Brewster
This is at least the second time that Ann Brewster had worked for Joe and Jack although the first time seemed to have been limited to a single piece (Chapter 9). As far as I know she is the only female artist that ever worked for Simon and Kirby but then again there were not many women in the comic book field. Brewster’s talents was recognized by Joe and Jack because she was one of the few artists to be used for Prize romance covers. I am not sure whether this resulted in any financial gain for Ann as her covers were created from stats made from her splashes. That it was the splashes that were the source is shown by the “original” of the cover for Young Romance #79 that is part of Joe Simon’s collection.

Young Love #67 (October 1955) “The Desperate Time”, art by Marvin Stein
With all the influx of new and returning artists during this last year it is surprising that it did not include more work by Marvin Stein. But Marvin does show up in a couple of stories late in 1955. Frankly I was not enthusiastic about much of Stein’s romance work although he had gotten better just before he stopped regularly providing work to Joe and Jack in 1952 (Chapter 16). Marvin returns as a much improved artist from the experience he accumulated as the lead artist for Headline and Justice Traps the Guilty (during the period when these titles were not produced by Simon and Kirby). The women that Stein would now draw were attractive and natural looking. While his drawing and inking has greatly improved Marvin still lacks the ability or inclination to depict intimacy; a serious failing in the romance genre. I am not overly enthusiastic about his romance art I find his work in the crime genre to be exceptional (I will be covering this in a future post).

In Love #6 (July 1955) “A Typical Teen Ager”, art by Art Gates
Art Gates has often been included in recent chapters of the Art of Romance however they were examples of his more realistic style. But I thought I would include one of his gag strips from In Love. Although as we have seen Gates did more realistic comic book art my impression is that he received more work doing gag features. But whatever the style Gates seemed to specialize in short one or two page features.

Young Love #67 (October 1955) “Hazardous Honeymoon”, art by Bill Benulis
While I cannot identify a number of the studio artists from this period there are some that I believe I can and so I will include some examples. “Hazardous Honeymoon” is unsigned but I still believe it was done by Benulis. Benulis style has a more modern look compared to most artists working for the S&K studio but he did not do a lot of work for Joe and Jack.

Young Love #68 (December 1955) “Echo of a Dream”, art by Harry Lazarus
I admit I might not have included “Echo of a Dream” in this chapter had it been unsigned. This is the only piece that I know of that Lazarus did for Simon and Kirby but he also did a story for Justice Traps the Guilty about the same time.
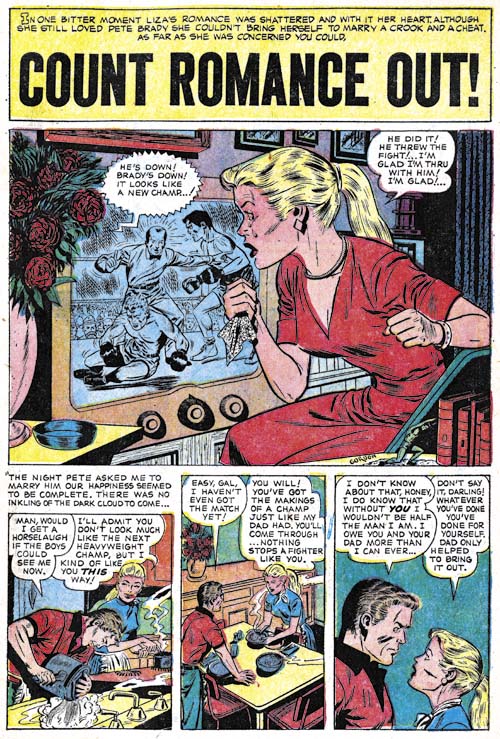
Young Brides #24 (September 1955) “Count Romance Out”, art by Al Gordon
Al Gordon is another artist who I might not have provided an example image for had he not signed the work. I do not want to give the impression that I thinks he or any of the unidentified artists are not competent it is just that in most case I cannot get to excited about them either. Gordon also do some work for Bullseye.

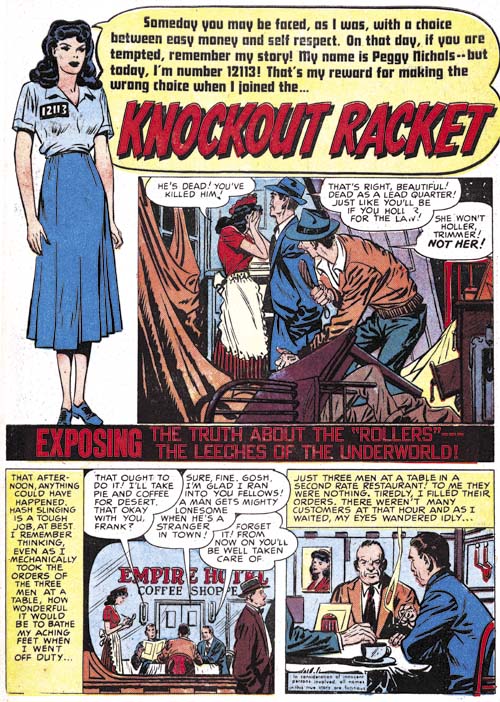
In Love #6 (July 1955) “I Deeply Regret”, art by unidentified artist
The period covered by this chapter does not seem to have much art purchased from other failing publishers. Such art picked up from failing romance titles seemed to be a significant feature of the comics covered in the previous two chapters. So far the only one I recognized for this chapter was “I Deeply Regret”. The lettering does not seemed to have been done by Ben Oda who was still the only letterer that Simon and Kirby used. That the lettering was not Oda’s is particularly obvious in the caption found in the splash. The floating captions with the unusual large first letter are also rather unique. I suspect with some searching it should be possible to identify the original source for this story.

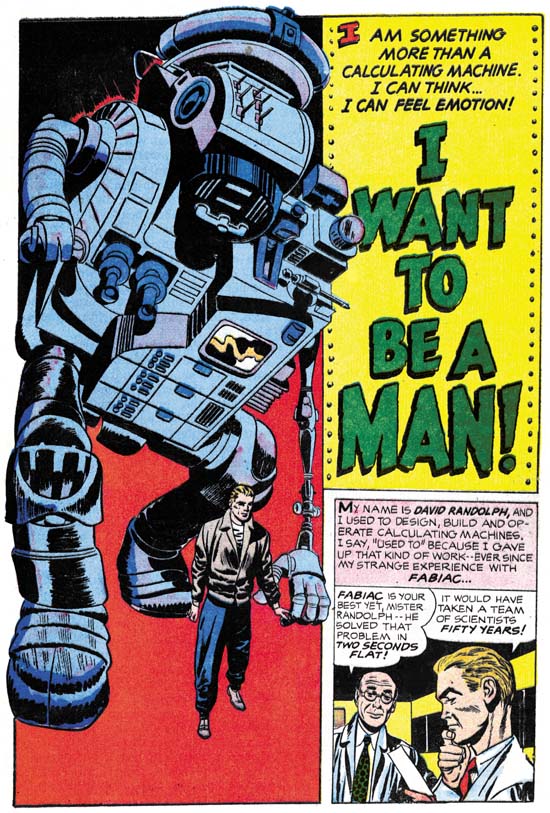
I Love You #7 (September 1955), pencils by Jack Kirby
I wonder whether it was ever Charlton’s intention to continue to publish Simon and Kirby’s former Mainline titles? Perhaps they only wanted to pick up some finished art cheap and get the second class mailing licenses. Whatever their original plans were, Charlton replaced In Love with a new title, I Love You. Since the I Love You issue number picked up from where In Love left off it certainly was using In Love’s mailing license. There was even a cover by Jack Kirby, although not one of his best efforts. The interior art was done by different artists from those previously used by the Simon and Kirby studio. I presume they are all artists that had been working for Charlton. I Love You would become a long running Charlton romance title.

Young Brides #25 (November 1955), art by Joe Simon?
The contents of Young Brides #25 was very distinctive for reasons that I will discuss below but even the cover is rather unique. For most of the period covered in this chapter the covers were created by a small group of studio artists (Bill Draut, Mort Meskin and Ann Brewster). This was also true during the period covered in the previous two chapters except the list of artists also included John Prentice and Bob McCarty. The cover for Young Brides #25 was distinctive because it was one of two covers that clearly was not done by any of the previous cover artists. The inker for the cover included the use of picket fence crosshatching (Inking Glossary) which suggests the possibility that Jack Kirby may have been involved. Picket fence crosshatching was one of the techniques of the studio style that typically was used on Kirby’s pencils. I will not completely rule out Kirby having penciled the two figures but I am do not find them convincing examples of his drawing style either. However the dog in the background strongly reminds me of Joe Simon’s work and so I am questionably crediting this cover to him. If true this is one of the few covers that Joe did during the Simon and Kirby collaboration.

Young Brides #25 (November 1955) “Cafe Society Lover, pencils by Jack Kirby
Young Romance #79 (October 1955) included a short piece (“Problem Clinic”) by Jack Kirby. The piece itself is not all that good; perhaps spoiled by poor inking (I have questionably credited the inking to Marvin Stein). However it marked the return of Kirby to the Prize romance titles from which he has been completely absent for about a year.
Jack Kirby next appeared in Young Brides #25 (November 1955). But this issue was odd because it contained three full stories drawn by Jack; an unusually high number. These stories are all much better than his “Problem Clinic” from last month’s Young Romance #79. Perhaps this is due to a better inking job. While I cannot rule out Jack providing some touch-ups, the spotting does not appear to have been done by Kirby.

Young Romance #80 (December 1955) “Old Enough to Marry”, pencils by Jack Kirby
Young Love #68 and Young Romance #80 both came out in December 1953. YL #68 was very much the same as most of the issues discussed in this chapter; a Meskin cover and story art by Meskin, Draut, McCarty, Stein and Lazurus. YR #80 was something entirely different; not only did Jack draw the cover he also penciled every story.
A short comment about the splash for “Old Enough to Marry”. At a glance it might appear that Jack has returned to the old confessional splash layout where a character introduces the story with his speech balloon containing the title. But the older man’s speech is actually part of the story. Other studio artists had stopped using the story splash format. If he was aware of that, Kirby was undeterred and with good reason. Jack may not have been doing much romance art during the previous year but he certainly has not lost his touch.
I will close this chapter with a good news, bad news section. The bad news first. Simon and Kirby productions will never be the same. One of the fundamental themes of this blog is that Simon and Kirby productions are not just Jack drawing and Joe inking. What Simon and Kirby did was much, much more. They put together entire contents and the studio artists they employed played an important part in provided those comics with varied and interesting content. While we will see some of this artists again under special circumstances and different venues, the absence of so many artists from future Simon and Kirby productions begs for an explanation. I can offer two possibilities. The first is that future Simon and Kirby productions, which were all romance work, seems to have been done on the cheap. The artists used in the future were on a whole not of the same caliber as those previously used. Lower pay made working for Simon and Kirby not as attractive as it was previously. The second explanation for the missing studio artists was the sudden termination of any work for 1956. The entire comic industry was collapsing and this included the Simon and Kirby studio. I do not know precisely when the actual studio closed but I believe it had done so by the end of 1955. If not then certainly by the end of 1956 when Jack Kirby had begun doing freelance work for DC and Atlas. It must have been a shock for the studio artists that the work offered by Simon and Kirby came to a sudden end. Joe Simon has said that all the artists were paid and I believe him but I wonder if the cash flow problems may have meant that for some the payment was delayed. In any case I suspect the sudden end of it all left many of the artists with hard feelings.
Now the good news. Not only will Simon and Kirby productions will never be the same but for the next year they are going to be unlike anything that was done before. The Prize romance titles will for the most part be drawn by Kirby alone. Such all, or near all, Kirby titles have happened in the past but under special circumstances. For instance the early issues of Boys’ Ranch and Fighting American were almost entirely by Kirby. It was part of the Simon and Kirby modus operandi that Jack would dominate the initial issues of a new title. But the Prize romance titles were hardly new; Young Romance had been running for over 8 years. Such a long stretch of all Kirby comics was completely unprecedented. Not only do we get a lot of Kirby but he was in great form; Jack came back to romance work revitalized. We will even get to see numerous examples of Kirby inking his own pencils. This is more unusual than many Kirby fans think. In the past the studio provided assistants and inking was done like a production line with different hands performing different chores. when a piece is said to be inked by Kirby even in this blog what this really means is that Jack provided the finishing touches. Now that the studio was gone Jack got less assistance and he did more of the inking himself. He also developed an inking style that was quicker but still pleasing. I have previously written about this style (Jack Kirby’s Austere Inking) and happily I now will get a chance to show some more. I am sure that the next few chapters of the Art of Romance will please Kirby fans.
Chapter 1, A New Genre (YR #1 – #4)
Chapter 2, Early Artists (YR #1 – #4)
Chapter 3, The Field No Longer Their’s Alone (YR #5 – #8)
Chapter 4, An Explosion of Romance (YR #9 – #12, YL #1 – #4)
Chapter 5, New Talent (YR #9 – 12, YL #1 – #4)
Chapter 6, Love on the Range (RWR #1 – #7, WL #1 – #6)
Chapter 7, More Love on the Range (RWR #1 – #7, WL #1 – #6)
Chapter 8, Kirby on the Range? (RWR #1 – #7, WL #1 – #6)
Chapter 9, More Romance (YR #13 – #16, YL #5 – #6)
Chapter 10, The Peak of the Love Glut (YR #17 – #20, YL #7 – #8)
Chapter 11, After the Glut (YR #21 – #23, YL #9 – #10)
Chapter 12, A Smaller Studio (YR #24 – #26, YL #12 – #14)
Chapter 13, Romance Bottoms Out (YR #27 – #29, YL #15 – #17)
Chapter 14, The Third Suspect (YR #30 – #32, YL #18 – #20)
Chapter 15, The Action of Romance (YR #33 – #35, YL #21 – #23)
Chapter 16, Someone Old and Someone New (YR #36 – #38, YL #24 – #26)
Chapter 17, The Assistant (YR #39 – #41, YL #27 – #29)
Chapter 18, Meskin Takes Over (YR #42 – #44, YL #30 – #32)
Chapter 19, More Artists (YR #45 – #47, YL #33 – #35)
Chapter 20, Romance Still Matters (YR #48 – #50, YL #36 – #38, YB #1)
Chapter 21, Roussos Messes Up (YR #51 – #53, YL #39 – #41, YB #2 – 3)
Chapter 22, He’s the Man (YR #54 – #56, YL #42 – #44, YB #4)
Chapter 23, New Ways of Doing Things (YR #57 – #59, YL #45 – #47, YB #5 – #6)
Chapter 24, A New Artist (YR #60 – #62, YL #48 – #50, YB #7 – #8)
Chapter 25, More New Faces (YR #63 – #65, YLe #51 – #53, YB #9 – #11)
Chapter 26, Goodbye Jack (YR #66 – #68, YL #54 – #56, YB #12 – #14)
Chapter 27, The Return of Mort (YR #69 – #71, YL #57 – #59, YB #15 – #17)
Chapter 28, A Glut of Artists (YR #72 – #74, YL #60 – #62, YB #18 & #19, IL #1 & #2)
Chapter 29, Trouble Begins (YR #75 – #77, YL #63 – #65, YB #20 – #22, IL #3 – #5)
Chapter 30, Transition (YR #78 – #80, YL #66 – #68, YBs #23 – #25, IL #6, ILY #7)
Chapter 30, Appendix (YB #23)
Chapter 31, Kirby, Kirby and More Kirby (YR #81 – #82, YL #69 – #70, YB #26 – #27)
Chapter 32, The Kirby Beat Goes On (YR #83 – #84, YL #71 – #72, YB #28 – #29)
Chapter 33, End of an Era (YR #85 – #87, YL #73, YB #30, AFL #1)
Chapter 34, A New Prize Title (YR #88 – #91, AFL #2 – #5, PL #1 – #2)
Chapter 35, Settling In ( YR #92 – #94, AFL #6 – #8, PL #3 – #5)
Appendix, J.O. Is Joe Orlando
Chapter 36, More Kirby (YR #95 – #97, AFL #9 – #11, PL #6 – #8)
Chapter 37, Some Surprises (YR #98 – #100, AFL #12 – #14, PL #9 – #11)
Chapter 38, All Things Must End (YR #101 – #103, AFL #15 – #17, PL #12 – #14)