I have recently posted on the initial issues of the Adventures of the Fly (here and here). There are still unidentified artists that penciled those issues (and more in the two Fly issues that followed). Identifying inkers is an even bigger challenged particularly because I am not that familiar with the brushwork of most of the possible inkers. However I recently noticed some inking in the Adventures of the Fly that was very familiar.

Adventures of the Fly #2 (September 1959) “Sneak Attack” page 2 (part), pencils by Jack Kirby
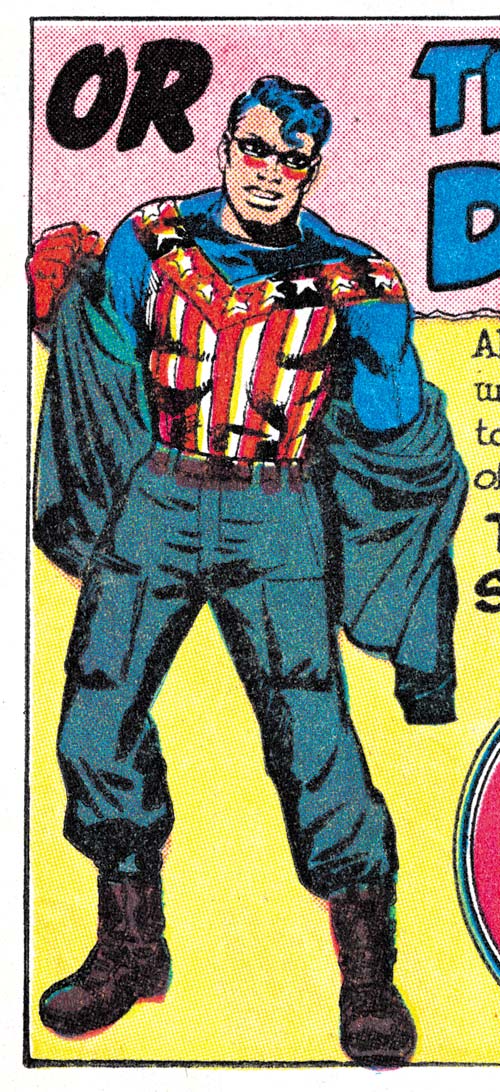
When I last wrote about “Sneak Attack” I attributed the pencils to Joe Simon. Well that was not the complete attribution. The bottom of the second page was an advertisement for the other Archie superhero comic, Double Life of Private Strong. The only art the ad contains is a standing figure of Private Strong changing into the Shield. It seems clear that the art was drawn by Jack Kirby. It is odd that the story and ad were done by different artists. I have studied the original art from Joe Simon’s collection and I can assure the reader that no cut and paste was performed to accomplish this.
The inking for the ad was really nicely done but unfortunately the details of which are obscured by rather poor printing. It is hard to see but the inner sides of both thighs were inked using picket fence crosshatching (Inking Glossary). The good news is that in the upcoming Simon and Kirby Superheroes volume from Titan “Sneak Attack” and the other stories I will be discussing here will be restored from the original art. Similarly robust picket fence brushwork was one of the characteristics of what I refer to as the Studio Style inking used during the Simon and Kirby collaboration. Not only did both Joe and Jack use this technique at that time but Mort Meskin did as well. I think, however, we can dismiss Meskin as the possible inker for the ad because he was no longer working with either Kirby or Simon and the inking here is a bit more spontaneous than was normal for Mort.

Adventures of the Fly #2 (September 1959) “Marco’s Eyes” splash (part), pencils by Jack Kirby
The spotting of the large figure of the Fly in the double page splash for “Marco’s Eyes is more finely worked than typical for either Simon or Kirby although either of them was certainly capable of it. Actually it is more finely worked than the inking found in any of the Fly art. So far I have not identified any brushwork in the figure that helps in determining an inking attribution.

Adventures of the Fly #2 (September 1959) “Marco’s Eyes” page 4, pencils by Jack Kirby
The story art for “Marco’s Eyes” shows an important characteristic that was typical of Studio style inking, what I refer to as shoulder blots (Inking Glossary). It is prominently shown in panels 2, 3 and 5 from page 4 but occurs elsewhere in the story as well. Numerous inkers have provided their shoulders with shadows but shoulder blots are distinct in that they occur on both shoulders regardless of how a shadow would expect to be cast. So far I have only seen Joe Simon and Jack Kirby make use of shoulder blots in their inking.

Adventures of the Fly #2 (September 1959) “The Master of Junk-Ri-La” page 2, pencils by Jack Kirby
There are no shoulder blots in “The Master of Junk-Ri-La” unless the shadow in panel 4 from page 2 is counted as one (but I am not inclined to do so). There are, however, a number of examples of course picket fence crosshatching. The first panel from page 2 shows a scallop pattern to the shadow on the boy’s arm. This scallop inking frequently showed up in Kirby’s inking. But the inking of the eyes and eyebrows of the boy look very much like the work of Simon.
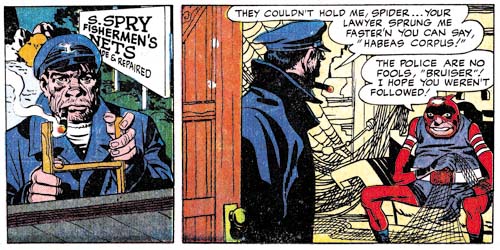
Adventures of the Fly #1 (August 1959) “Come Into My Parlor” story panels 3 and 4 from the double page splash, pencils by Jack Kirby
The double page splash and accompanying story panels of “Come Into My Parlor” also contains what looks like Studio style inking. Particularly note the spotting of the sailor from story panels 3 and 4. Observe the two cloth folds on the man’s shoulder in panel 4. These cloth folds show no indication of the tip of the brush which is a technique that was typical of Kirby’s inking. I am less convinced about the inking of the rest of the story. It should be kept in mind that it was common during the Simon and Kirby collaboration for Kirby to be involved with the spotting of the splash and leave the rest of the story to other inkers.
Studio style inking techniques are not limited to the four stories that I have discussed here. But their occurrence elsewhere in the first two issues of Adventures of the Fly seems limited to what looks like touch-ups of the work by other inkers. Such touch-up were almost certainly the work of Simon since Kirby was then a freelancer working from his house.
I only become confident about inking attributions after I have “lived” with them for some time. However it is my policy to present my current views in this blog even if they are likely to be subject to change. At this time I believe “The Master of Junk-Ri-La” was inked by Joe Simon. I am also fairly certain that Jack Kirby inked the splash pages of “Come Into My Parlor”. I am less confident about the inking attributions for the ad from “Sneak Attack” or “Marco’s Eyes”. I currently am crediting Kirby for that inking but I am bother about the frequent appearance of the tip of the brush in the inking which previously was not typical for Kirby although it was for Simon.